- Motivation:
- Problem Statement
- With the advent and proliferation of Deep Neural Networks (DNNs), there's a significant increase in computational demands. Managing these demands efficiently is crucial for the performance and scalability of DNNs.
- Traditional compilation processes for tensorized instructions, which are central to DNN computations, can be cumbersome and may not fully exploit hardware and software optimizations.
- To address the computational and memory challenges by unifying the compilation process for tensorized instructions. A unified approach can lead to better utilization of available resources and ease the integration of new instructions.
- Motivation
- Reducing multiple low precision to high
- Horizontal reduction
- Mixed precision
- Software abstraction of the kernel library for tensorized instructions that can be deployed on intel VNNI, ARM SVE, and NVIDIA Tensor Cores. Possibly for AMX now. Nowadays, they only have library compliance for tensorized instructions each time they upgrade the GPU/TPU/ASIC.
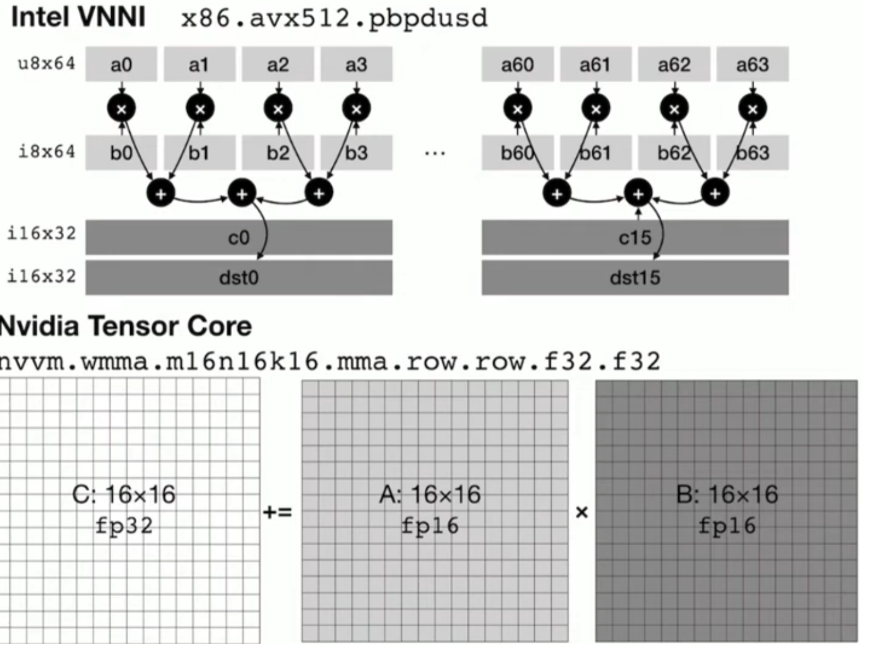
- Reducing multiple low precision to high
- Problem Statement
- Compiler Solution - The UNIT Framework - A virtual ISA abstraction:
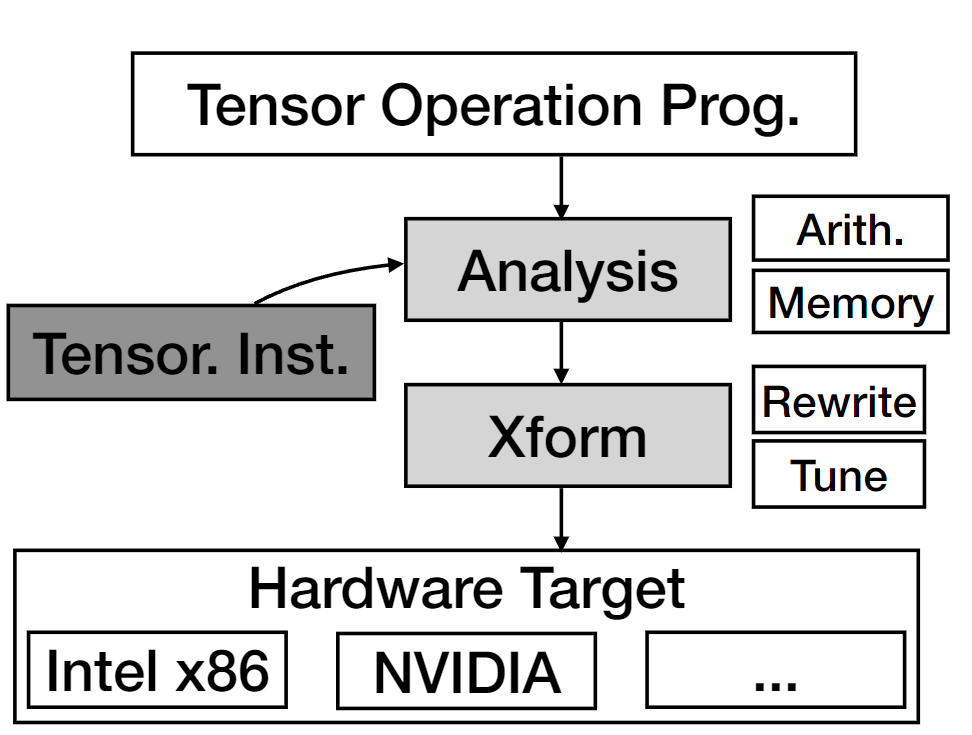
- Framework Overview
- The authors propose a compiler framework called UNIT to unify the compilation for tensorized instructions.
- At the heart of UNIT is a unified semantics abstraction which simplifies the integration of new instructions and allows for the reuse of analysis and transformations.
- Key Features
- Ease of Integration: The framework is designed to simplify the integration of new tensorized instructions.
- Reuse of Analysis and Transformations: By adopting a unified semantics abstraction, the framework facilitates the reuse of analysis and transformations, promoting efficiency.
- Translation of Memory Operations: The framework translates memory operations to tensorized instructions and do optimizations over this.
- Mixed Precision Data Types
- A notable approach to reducing computational and memory burden is the use of mixed precision data types. This approach is widely adopted and is integrated within the UNIT framework.
- Mixed Sized Data Types
- The authors also propose the use of mixed sized data types to reduce the computational and memory burden. This approach is also widely adopted and is integrated within the UNIT framework.
- Framework Overview
- Illustrative Example:

 We first use the Arithmetic Isomorphism for a single thread using split/tile reorder and unroll.
We first use the Arithmetic Isomorphism for a single thread using split/tile reorder and unroll. 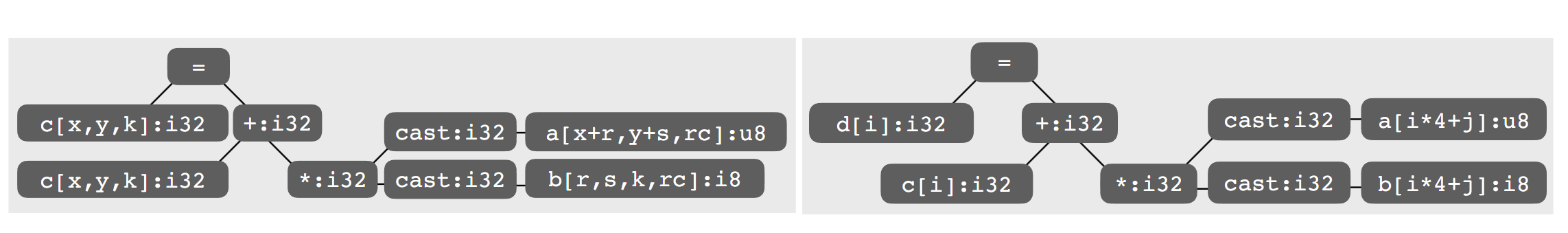 Then we have the Memory Isomorphism for intel VNNI, basically mark the loop invariant and lower to the other precision and other sized tensorized operations.
Then we have the Memory Isomorphism for intel VNNI, basically mark the loop invariant and lower to the other precision and other sized tensorized operations. 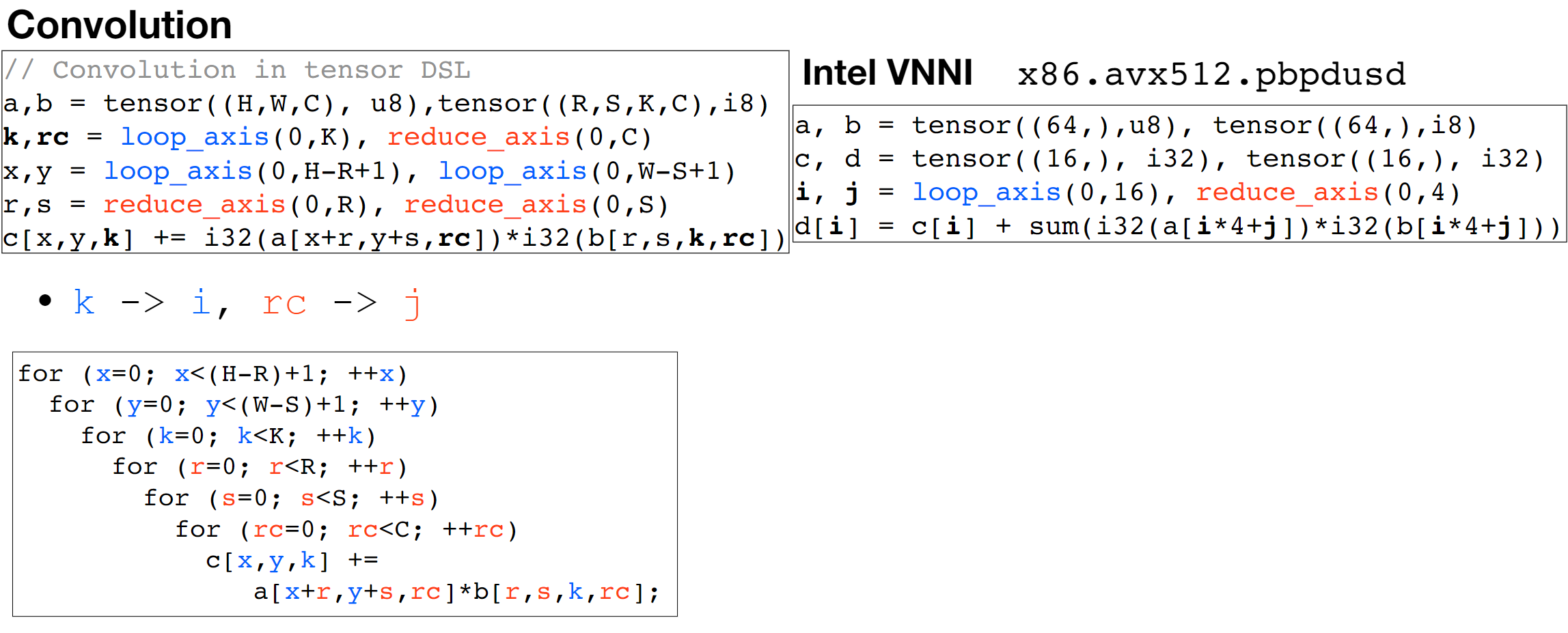
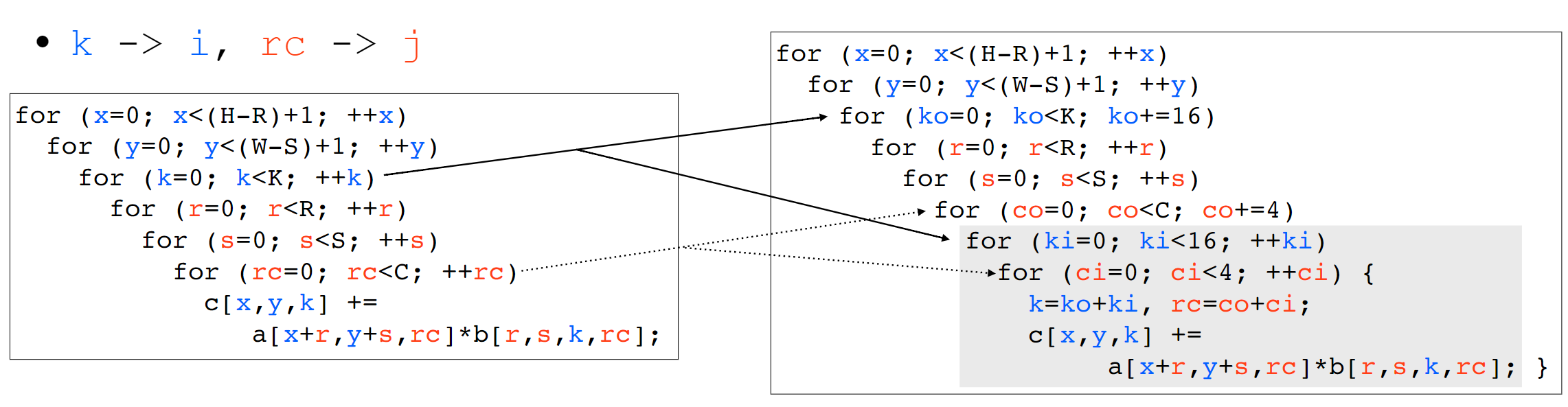
 Finally we do the transformation for Loop Recorganization for registers
Finally we do the transformation for Loop Recorganization for registers 
- Implementation and Key Results:
- The paper likely provides an implementation of the UNIT framework and evaluates its performance against traditional compilation processes. (Note: The actual implementation and evaluation details would be in the paper which wasn't accessible during the research.)
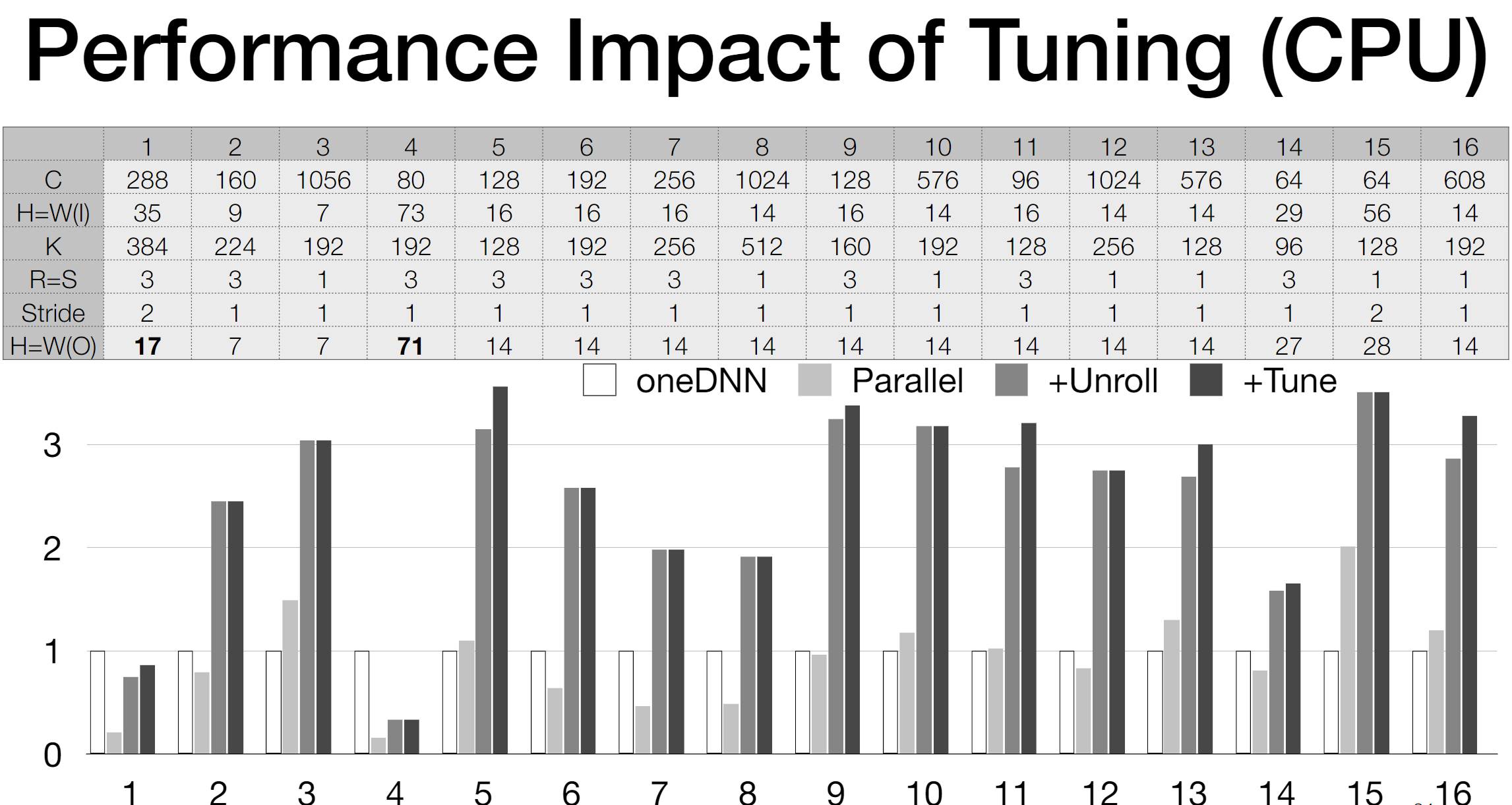
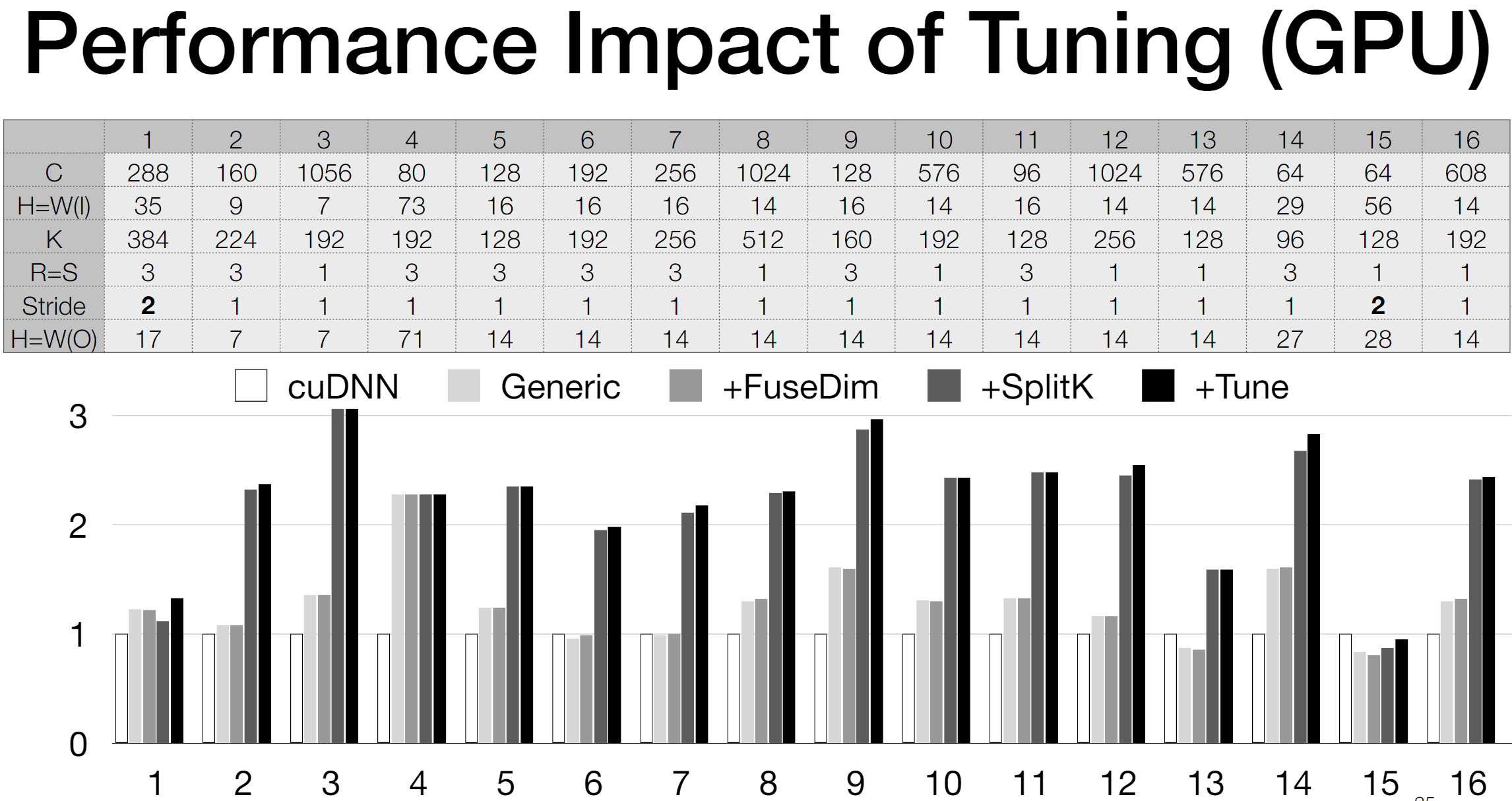
- The paper likely provides an implementation of the UNIT framework and evaluates its performance against traditional compilation processes. (Note: The actual implementation and evaluation details would be in the paper which wasn't accessible during the research.)
- Discussion and Future Directions:
- Benefits
- The UNIT framework, as per the authors, presents a viable solution to the challenges of compiling tensorized instructions efficiently, thereby addressing a critical aspect of DNN performance optimization.
- Implications
- The proposed framework could have broader implications for the field of DNNs, particularly in how tensor computations are handled in both hardware and software domains.
- Future Work
- The paper may suggest directions for future work to further enhance the UNIT framework or explore other optimizations in tensorized instruction compilation.
- Benefits
- Conclusion and Comments:
- The UNIT framework emerges as a significant contribution towards optimizing the compilation process for tensorized instructions, addressing the computational and memory challenges associated with DNNs.
- We need a vISA for dynamically JIT the vISA will be great for migrating the same code to different hardware rather than library compliance.