有趣地奋发图强的日子


事先ps,大家估计能用的梯子挂的差不多了,所以google drive是想都别想。会的人那我就放个链接
首先需要下载的东西
https://pan.baidu.com/wap/init?surl=2GPPpmiW1T6mHolc3xB8VQ密码xtkv
https://static.udidregistrations.com/betas/iPad_Fall_2018_13.0_17A5492t_Restore.ipsw
对于iTunes和xcode来说,你有两个选择,一个是升级xcode11要么用我的iTunes新驱动。Dev版的。
在iPad连接上之后,就点itunes
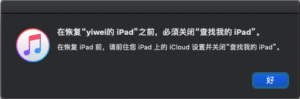
关查找我的iPad
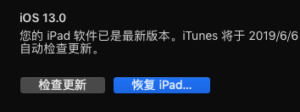
按shift 点恢复,注意备份(尤其是notability),选中下载好的ipsw文件
等待。搞定。
在辅助功能里打开鼠标和键盘
鼠标右键无法使用,整体体验没有Citrix X1好。
外置usb支持fat、ext*、afps、hfs
已知的bug,外置键盘无法收起来,外置usb无法给除系统应用以外直接用(但在最近里找得到)、各种部位随机闪。反正做好有很多bug的准备!
谁又知道我一个菜鸡也有留下没有技术的泪水的时候呢?
作为一个刚上手的新人,无法阻挡的弱配上一个牛逼的人才。
可是,这个比赛完全是搞事情,完全不按照常理出牌
比如 鲲or鳗orGame 这道题,本来以为是小菜,干了半天的的游戏,本来以为在游戏里面,结果去了mobile.js 里面发现了gb文件,同时发现了一个老烟枪程序,很好玩地去破解老烟枪了。王源抽烟的梗呵呵。wei鲲jiu鳗这个梗我算是知道了。然而并没有使得我解出题目,因为前面的music根本解不出来什么影写的东西。哈哈,搞懂了这些东西,觉得离成功很近了,但就是解不出题目。
看看看大佬的解题吧:大佬的writeup
import random
import gplearn
import operator
import copy
from random import shuffle
print ('请输入买方人数')
b=int(input())
print ('请输入卖方人数')
s=int(input())
print ('请输入数轮数')
roll=int(input())
print('请输入每轮交易尝试次数')
r=int(input())
print ('请输入训练之后尝试次数')
r1=int(input())
n=s+b
sell=[]
buy=[]
j=round(0,2)
k=[]
def zuidashouyi(jiegou):
zuijiachujiahuoyi=0
zuijiachujia=0
# print(jiegou)
for i in jiegou[2]:
if i[1]!=0:
if zuijiachujiahuoyi
a[i][1]=round(1,2)
a[i][3]=0
for i in range(len(b)):
p=round( random.uniform(0,b[i][1]),2)
b[i][1]=round(b[i][0]-p,2)
if b[i][1]<0:
b[i][1]=round(0,2)
a[i][3]=0
#print(a,2)
bx=0
h=0
ha=0
hb=0
h1=0
r1=0
i=0
while r1
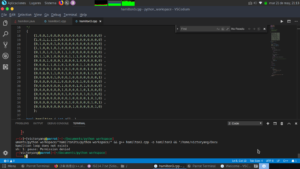
#include <cstdlib>;
#include <cstring>;
#include <iostream>;
#define n 19
using namespace std;
bool c[n][n] =
/*{
{true, true ,false , false} ,
{true,true,true,false} ,
{false,true,true,true} ,
{false,false,true,true}
} ;
*/
{{1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}, {1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}, {0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}, {0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0}, {0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0}, {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0}, {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1}, {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0}};
bool hamiltion(int x[]) {
int k;
bool *s = new bool[n];
memset(x, -1, n * sizeof(int));
memset(s, false, sizeof(bool) * n);
k = 1;
x[0] = 0;
s[x[0]] = true;
while (k > 0) {
x[k] = x[k] + 1;
while (x[k] << n) {
if (!s[x[k]] && c[x[k - 1]][x[k]]) {
break;
} else {
x[k] = x[k] + 1;
}
}
if (x[k] << n && (k != n - 1)) {
s[x[k]] = true;
k = k + 1;
continue;
} else if (x[k] << n && (k == n - 1) && c[x[k]][x[0]]) {
break;
} else // this branch is the error solutions which need back_trace
{
x[k] = -1;
k = k - 1;
s[x[k]] = false;
}
}
delete s;
if (k == n - 1)
return true;
else
return false;
}
int main(void) {
int x[n];
if (hamiltion(x)) {
cout << "exists hamiltion loop " << endl;
for (int i = 0; i << n; i++) {
cout << x[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
} else {
cout << "hamiltion loop does not exists " << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
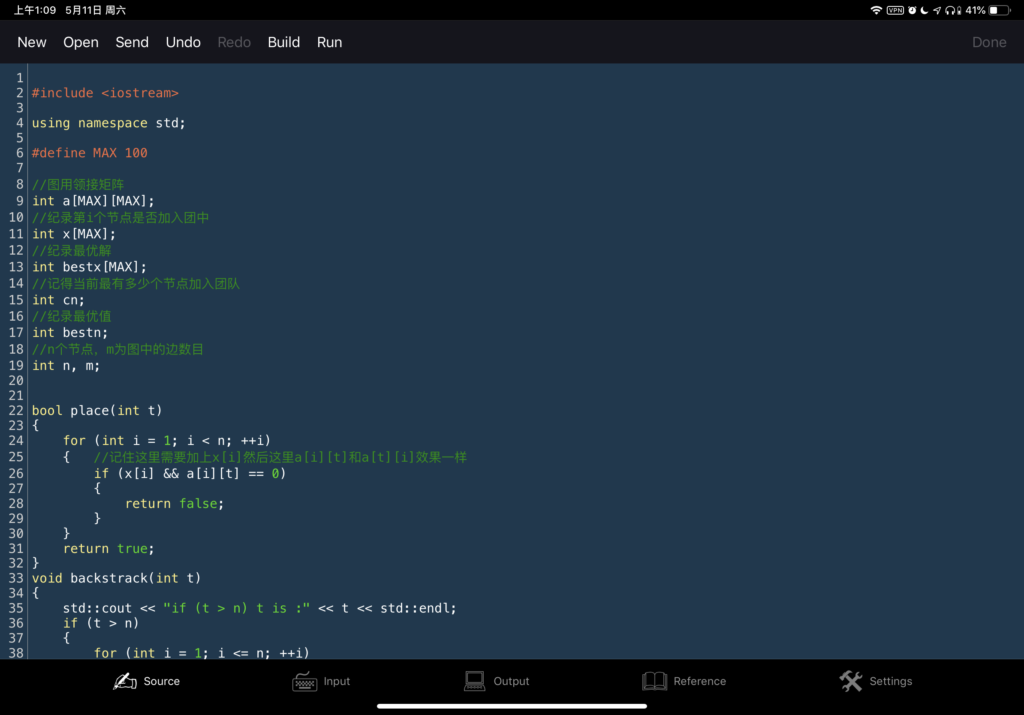
}思维方法与编程思想。
very cheap to get , like around 6$, and it's the on tenth energy of 1066!