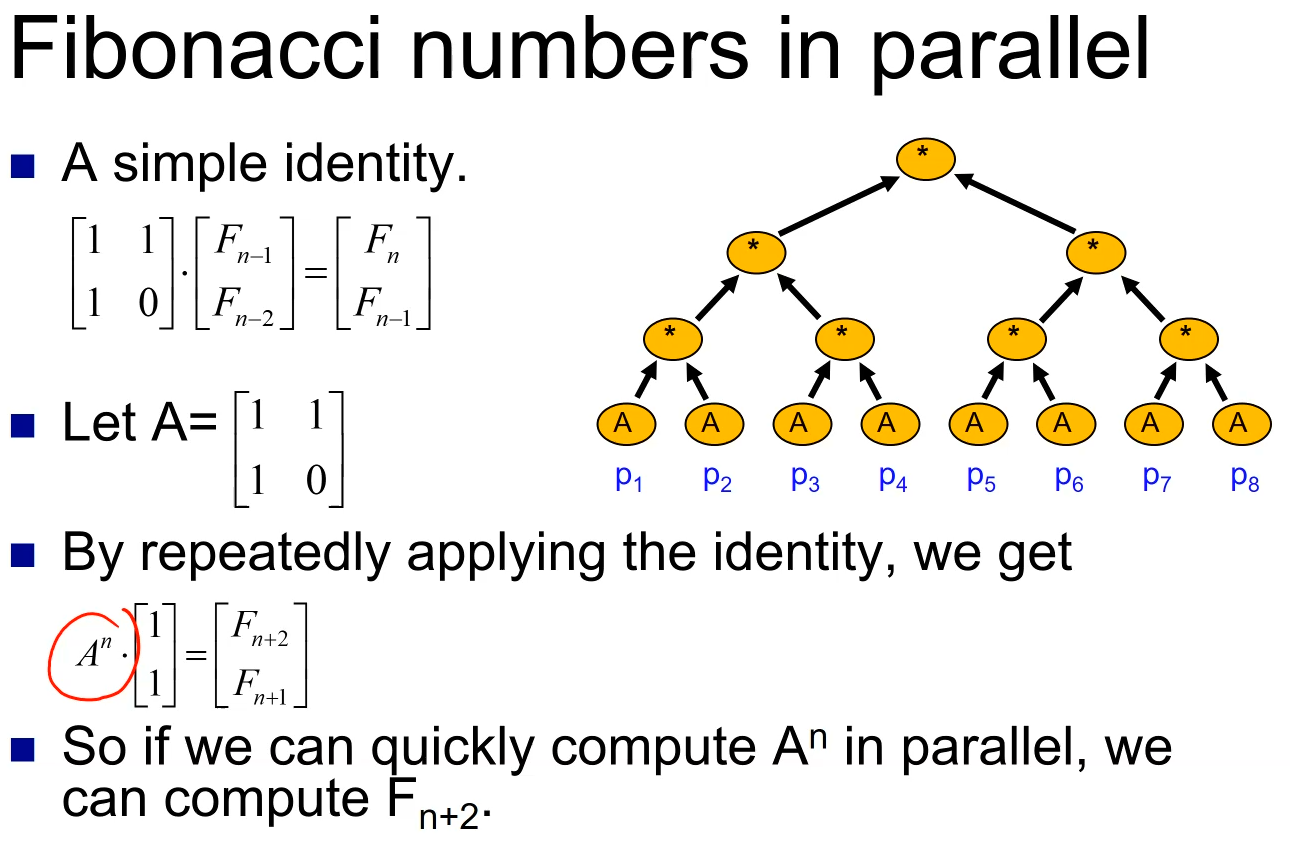
Intro
shared memory algorithm design
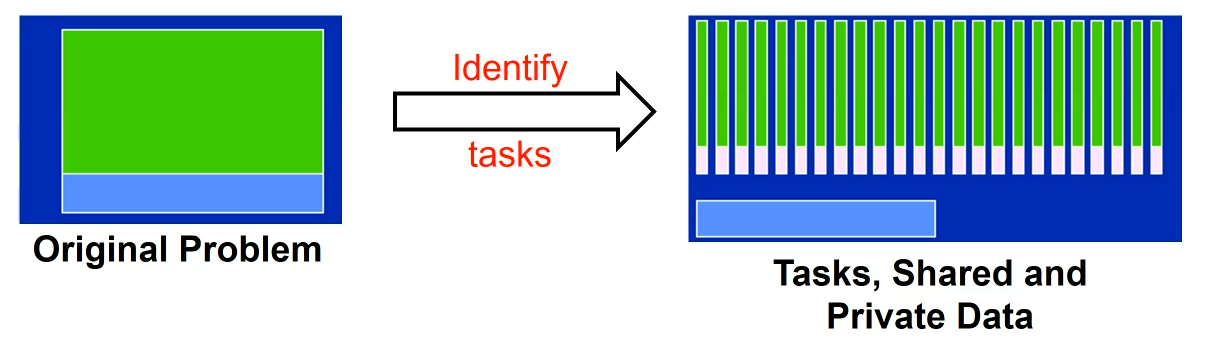
For non-shared memory algorithms, we have to utilize bararrier to gain data transformed.
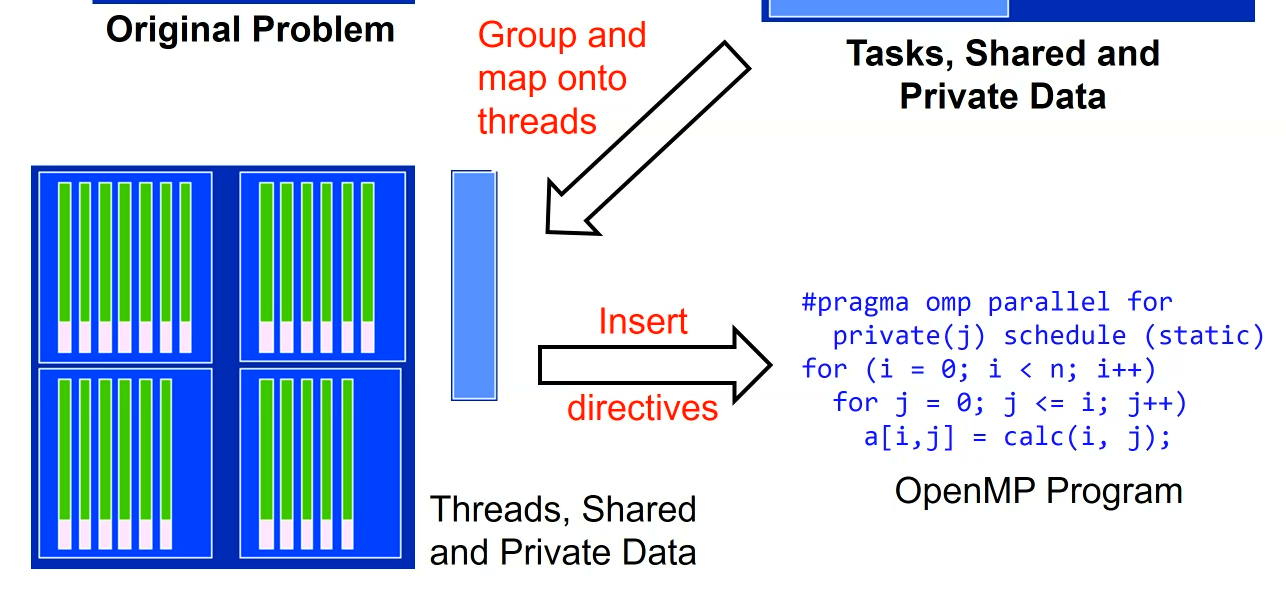
for shared memory database algorithm, we have to decide the group part of the task that shared memory a lot . Then just apply the inserting directives of omp or mpi
Design considerations
two main considerations lies in data dependence and load balance so we have to apply the following steps
- data dependence analysis
- static r dynamic and block r cyclic work assignment
- variable specification whether using shared private r reduction and row-wise r column-wise
- shared variables cause cache coherence traffic and much lower performance
- private and reduction variables don't need synchronization
- dimension mapping is more relying on the cache locality
Main Consideration for data dependence analysis
RAW & WAR & WAW
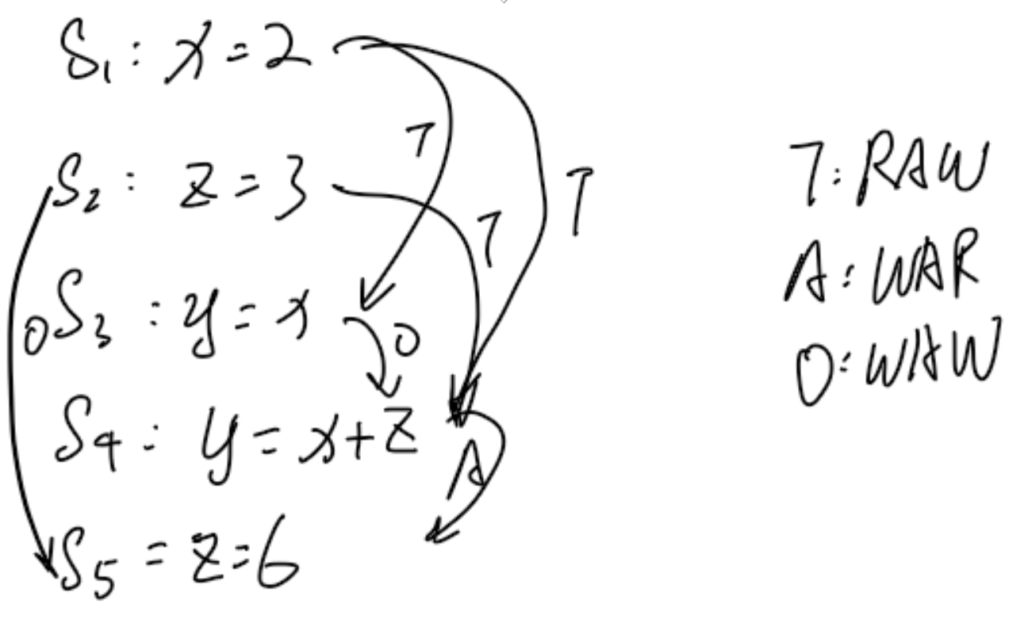
all the collations should be avoided though they might run into right situations
Goal is to we should run all the dependent situation on the same processor.
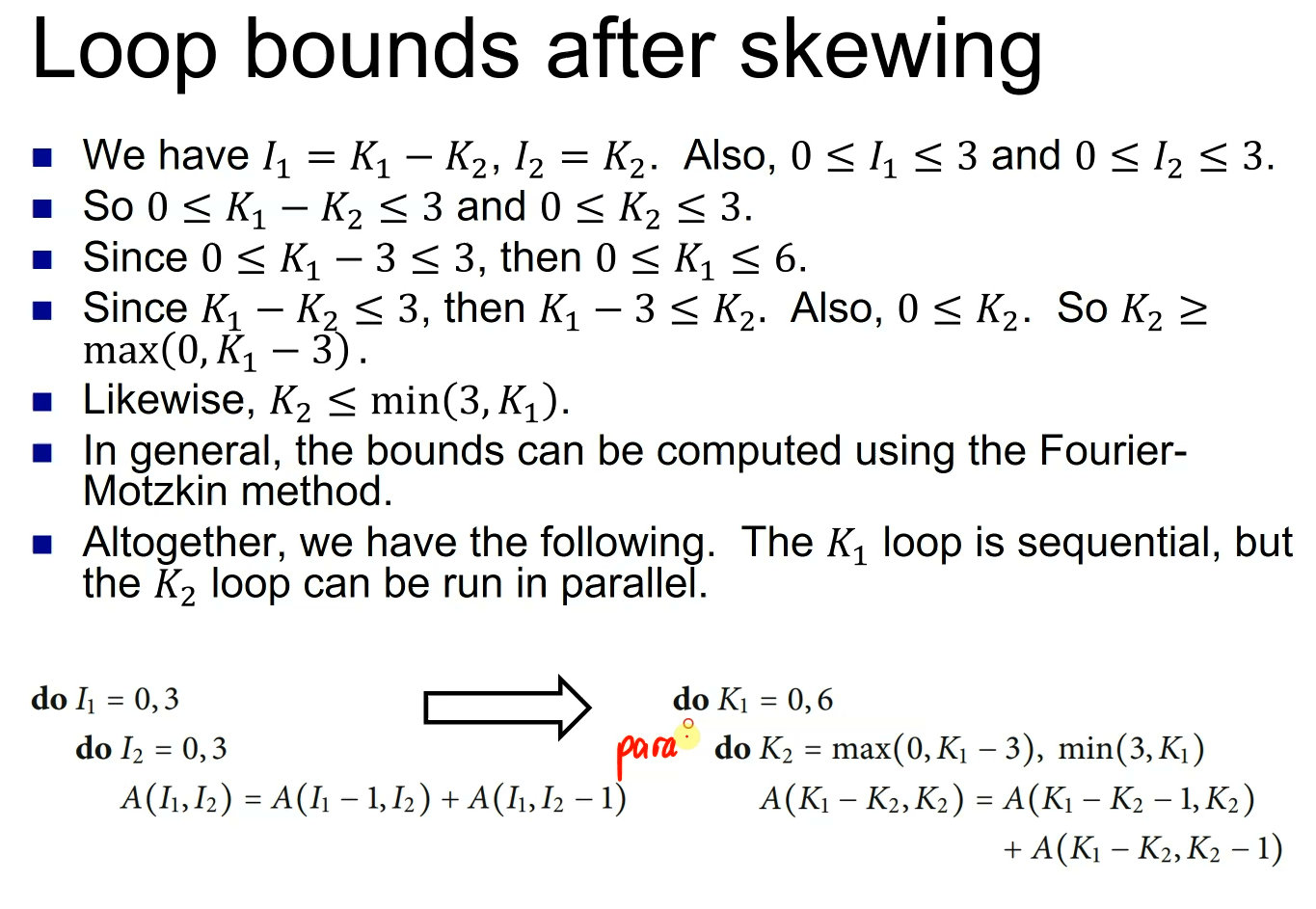
loop dependence analysis
- loop-carried dependence
- dependence exists across different iterations of loop
- loop-independent dependence
- dependence exists within the same iteration of loop
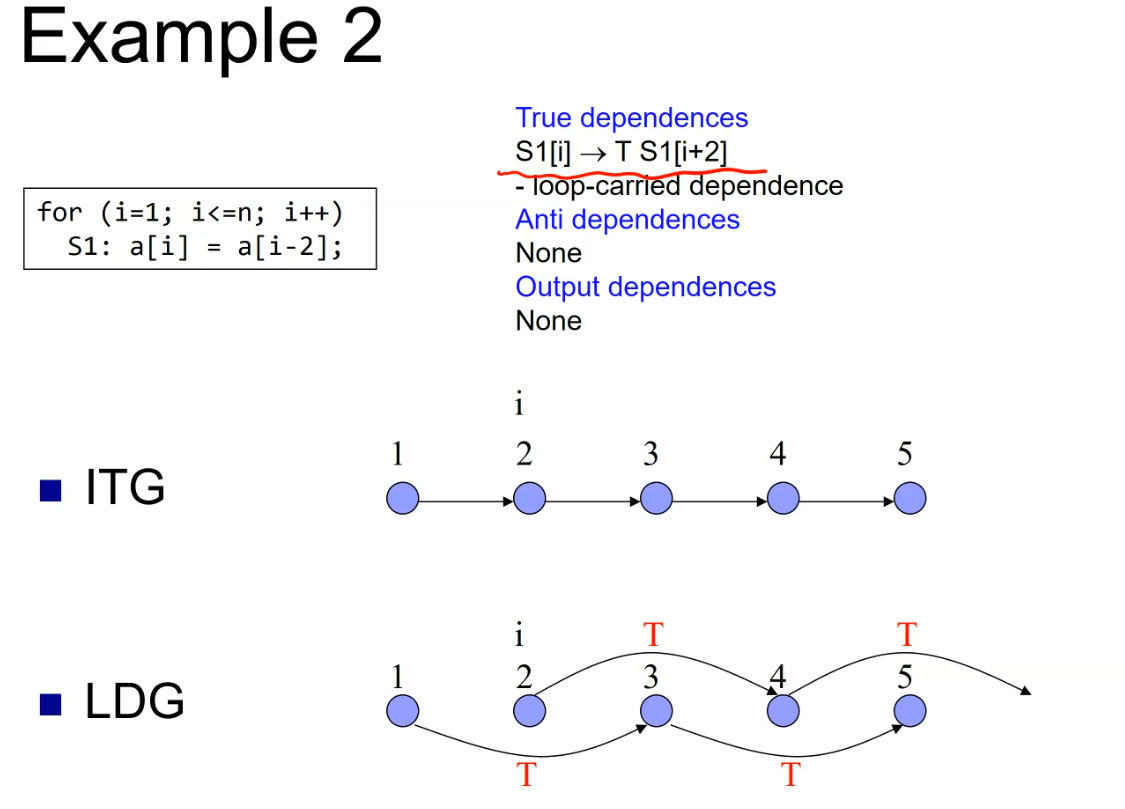
example
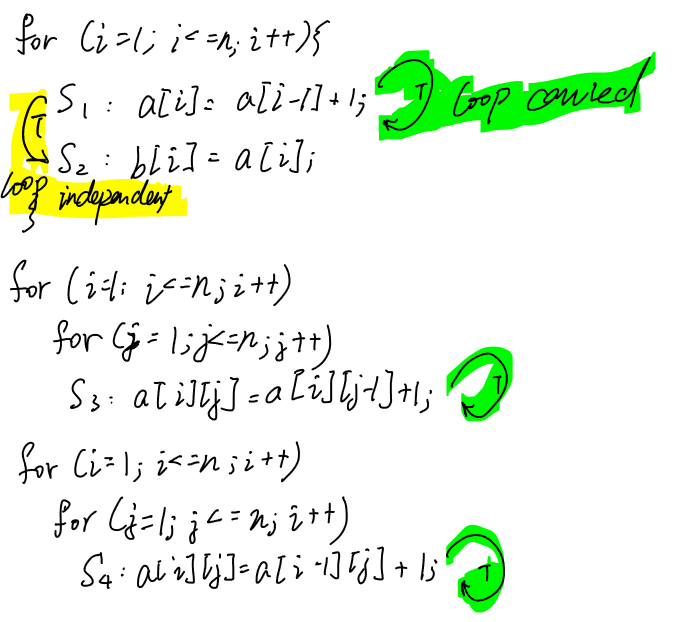
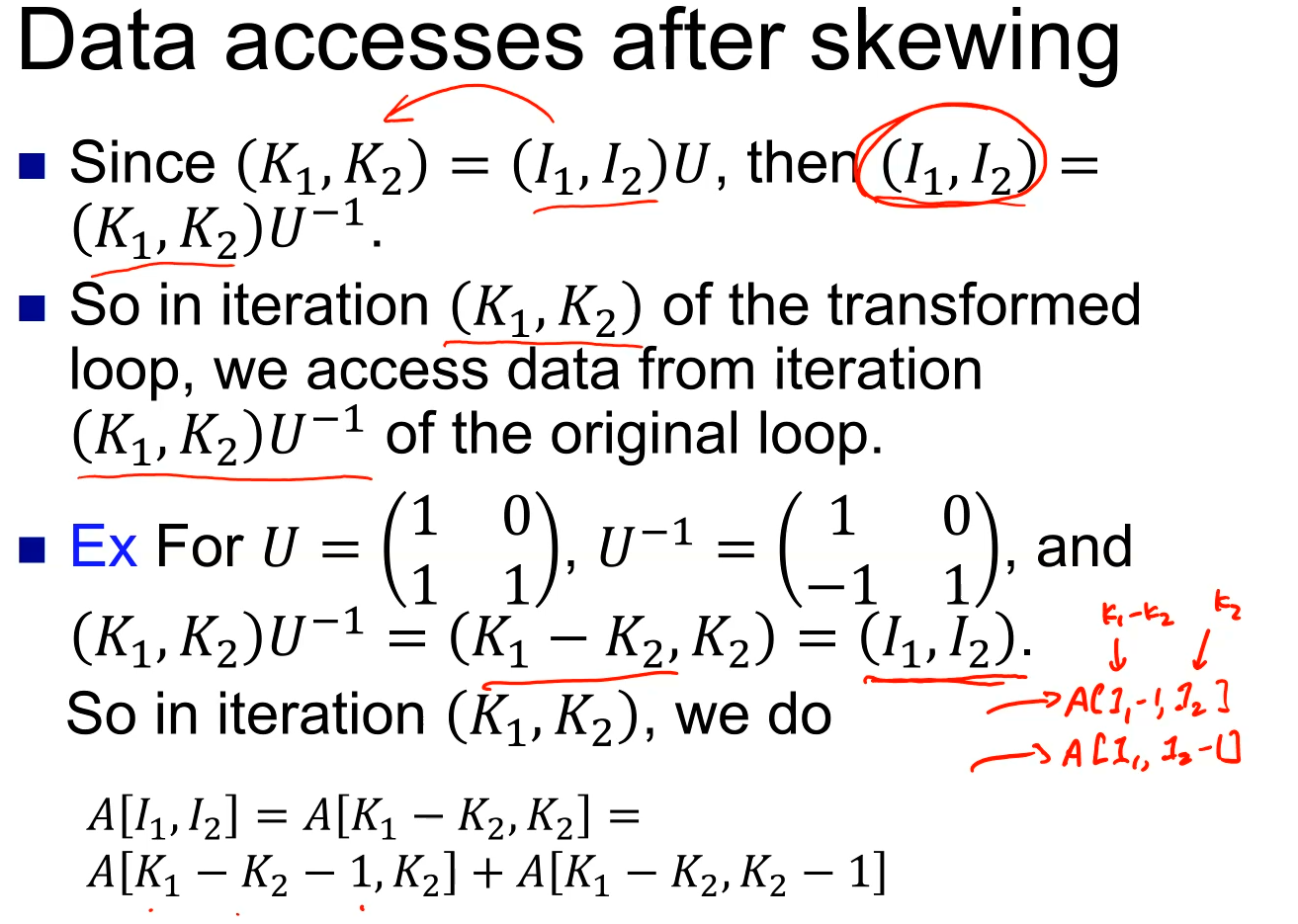
iteration-space traversal graph (ITG)
- iteration-space traversal graph is a line graph showing the order of traversal in the iteration space.
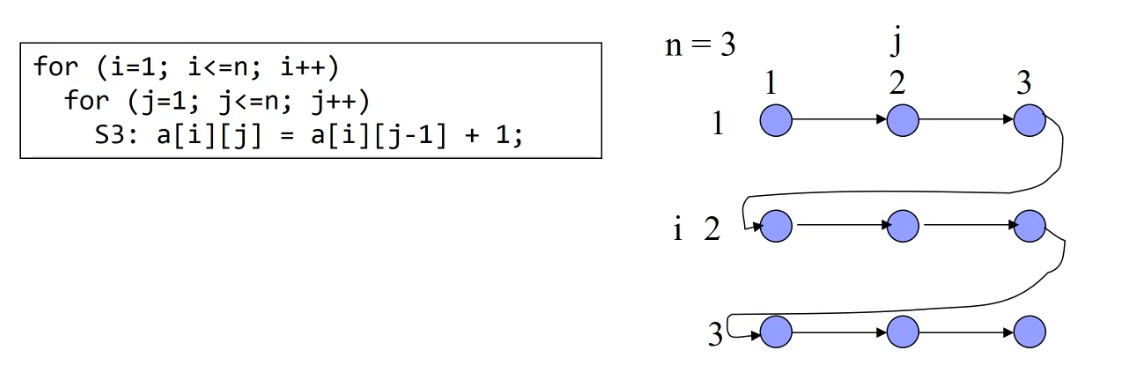
loop-carried dependence graph (LDG)
- Given the ITG, can determine the dependence between different loops.
- Loop-carried Dependence Graph (LDG) shows the loopcarried true/anti/output dependence relationships.
- Node in LDG is a point in the iteration space.
- Directed edge in LDG is the dependence.
- LDG helps identify parts of the loop that can be done in parallel.
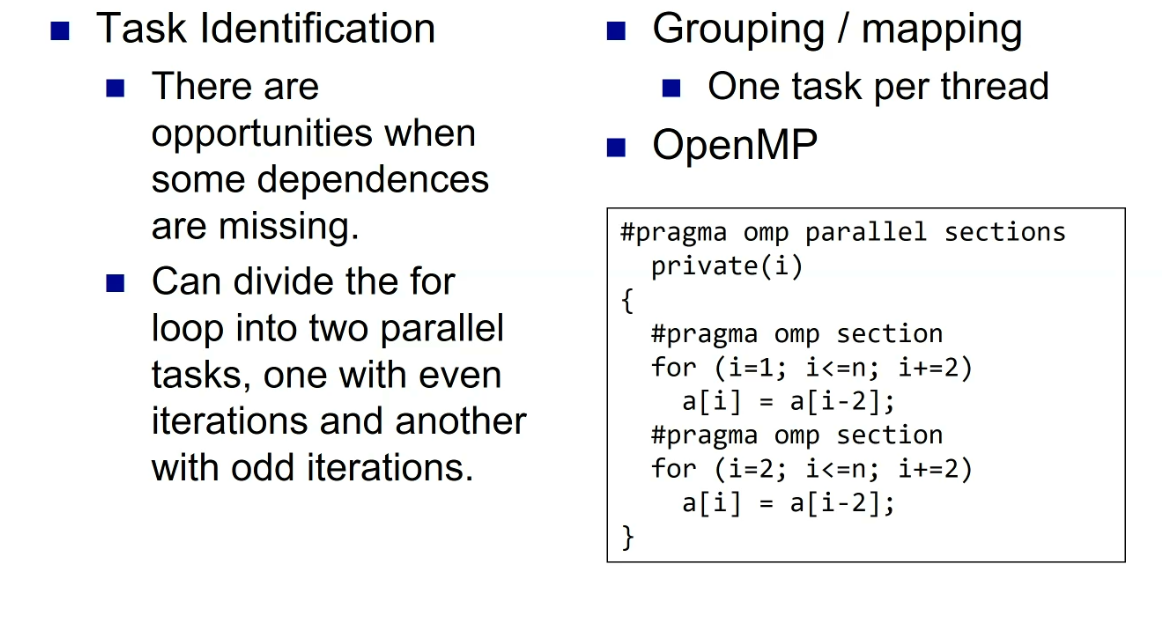
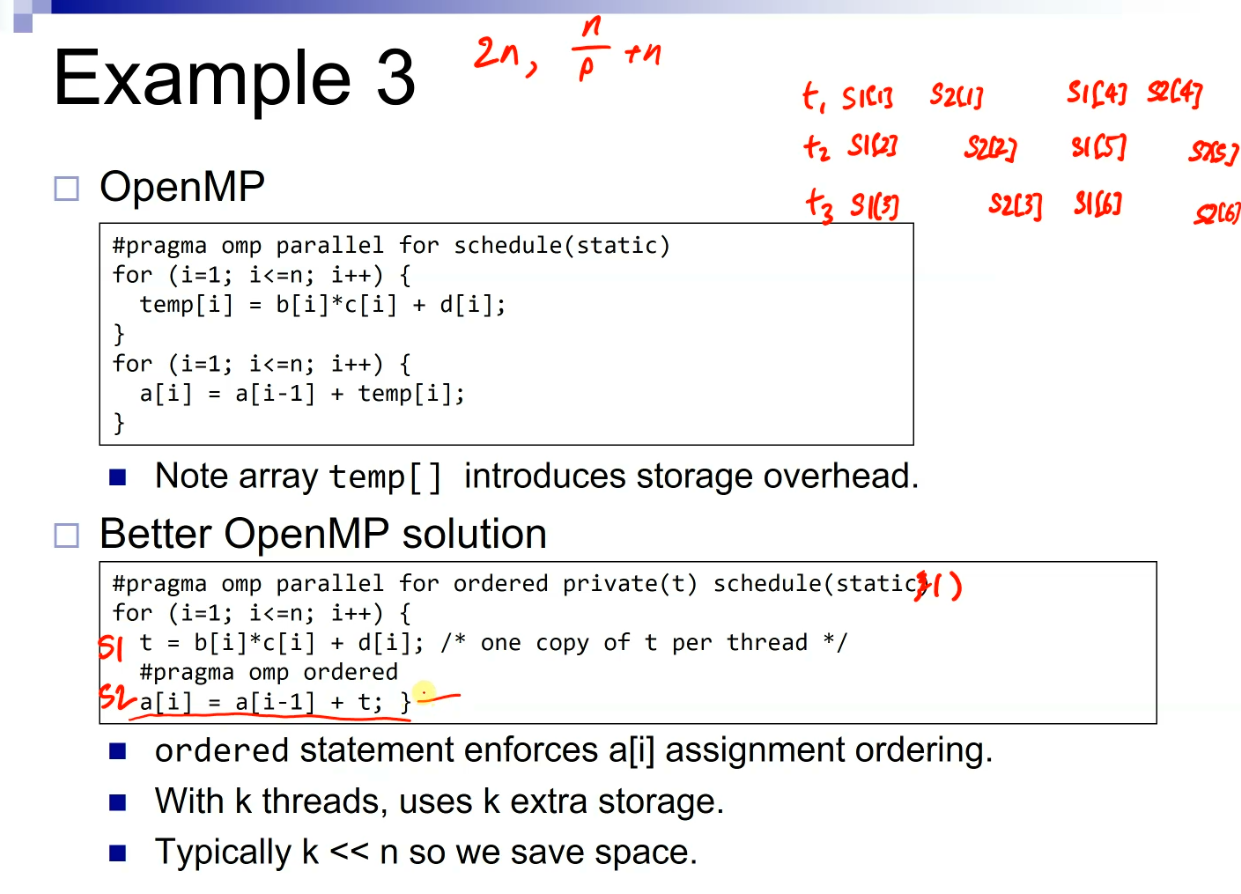
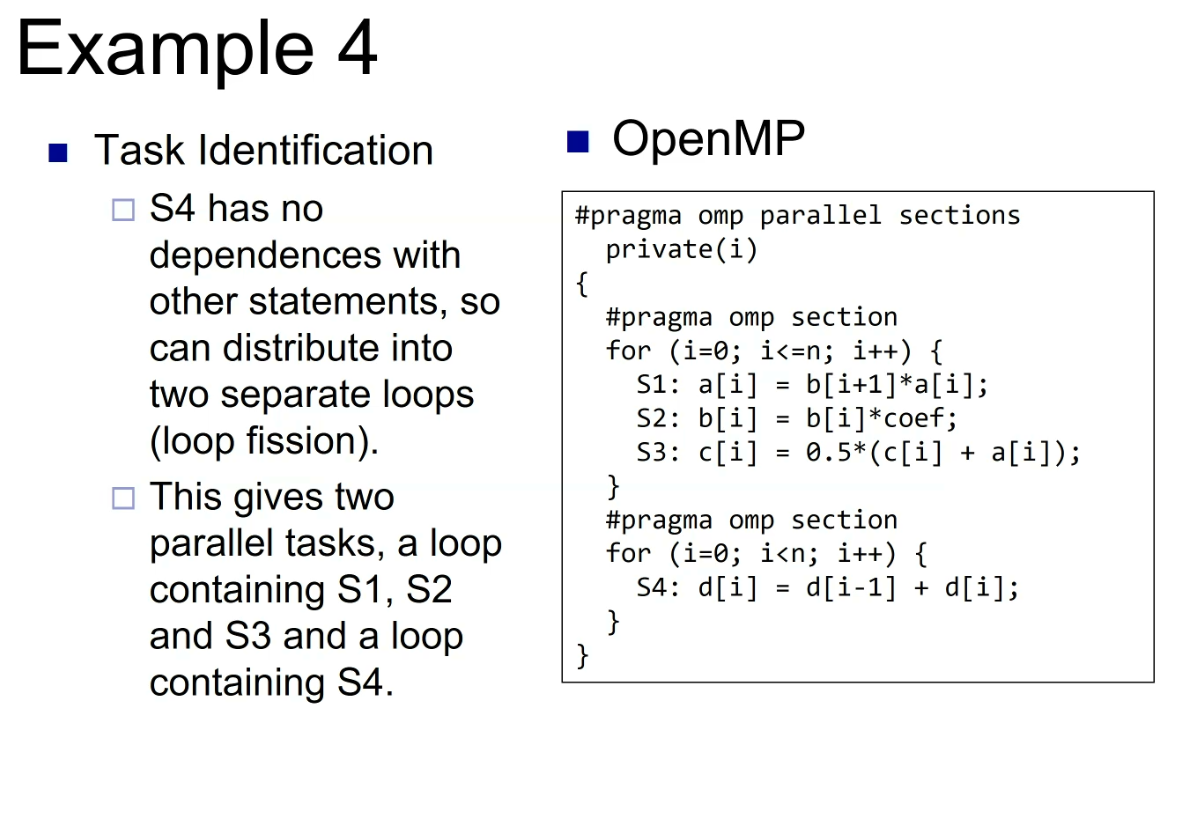
examples
Distance and direction vector
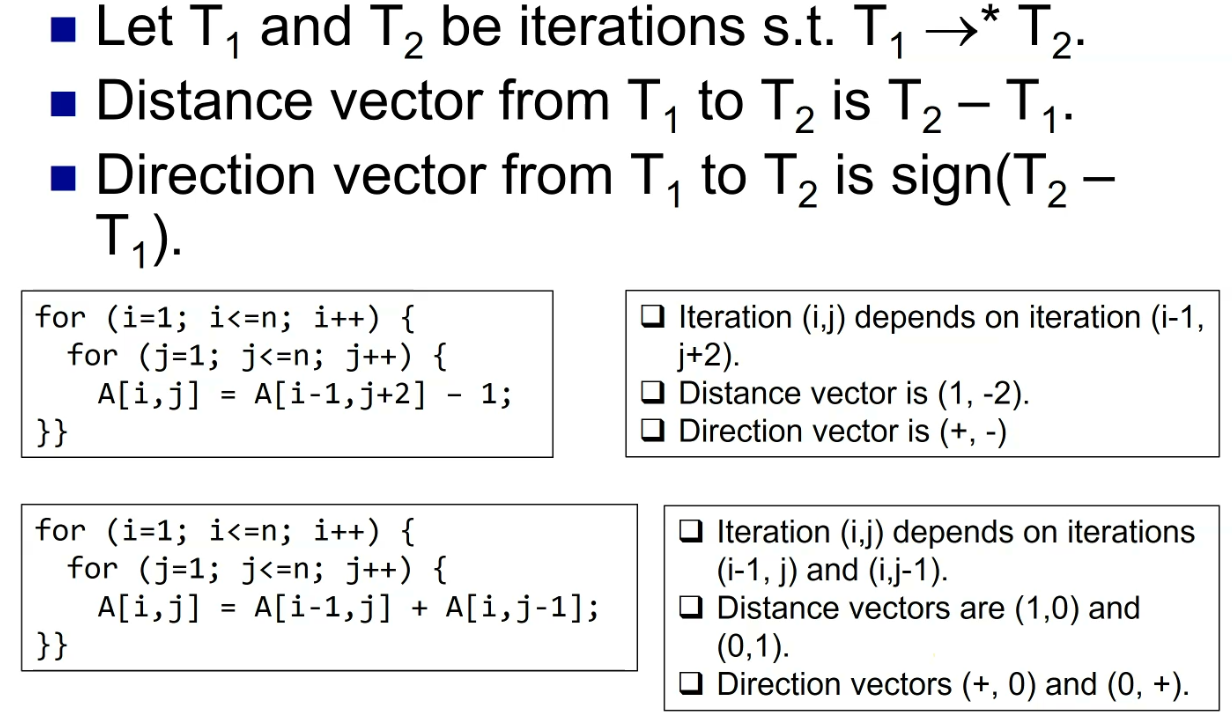
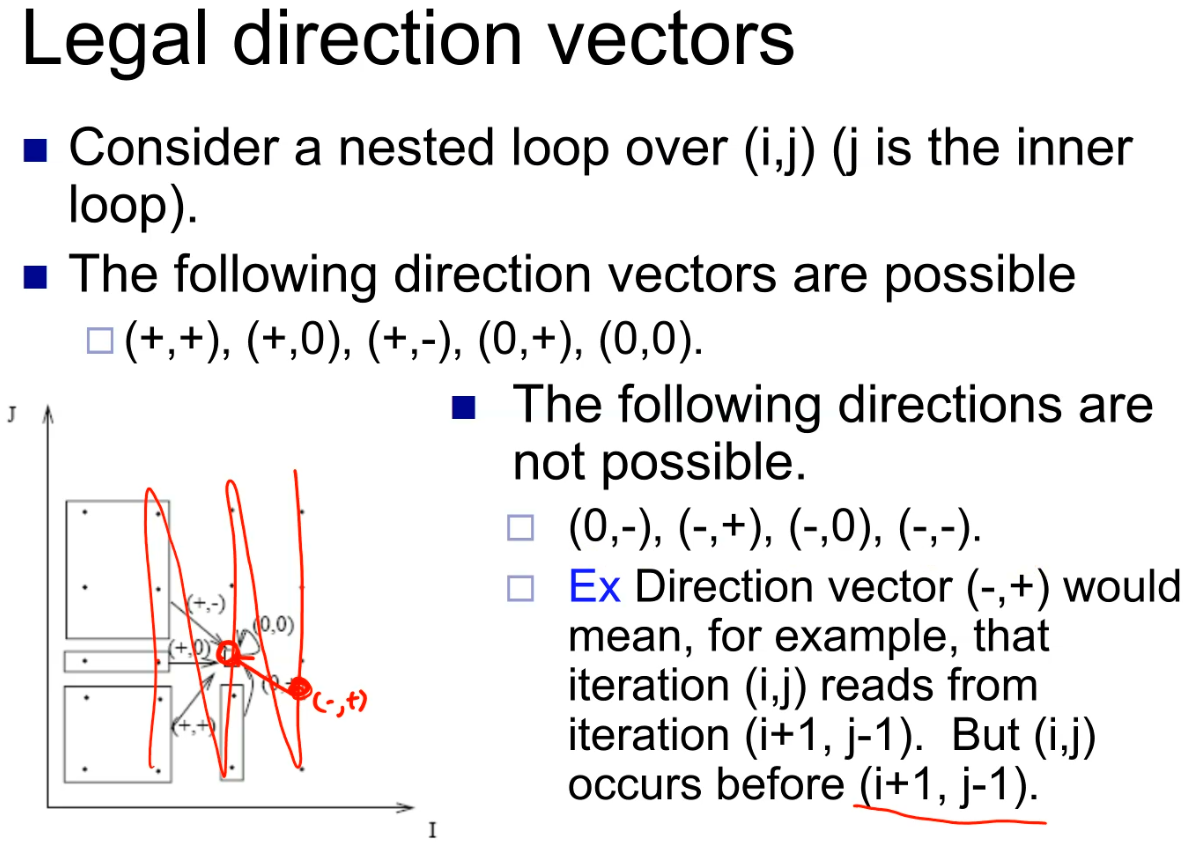
Loop
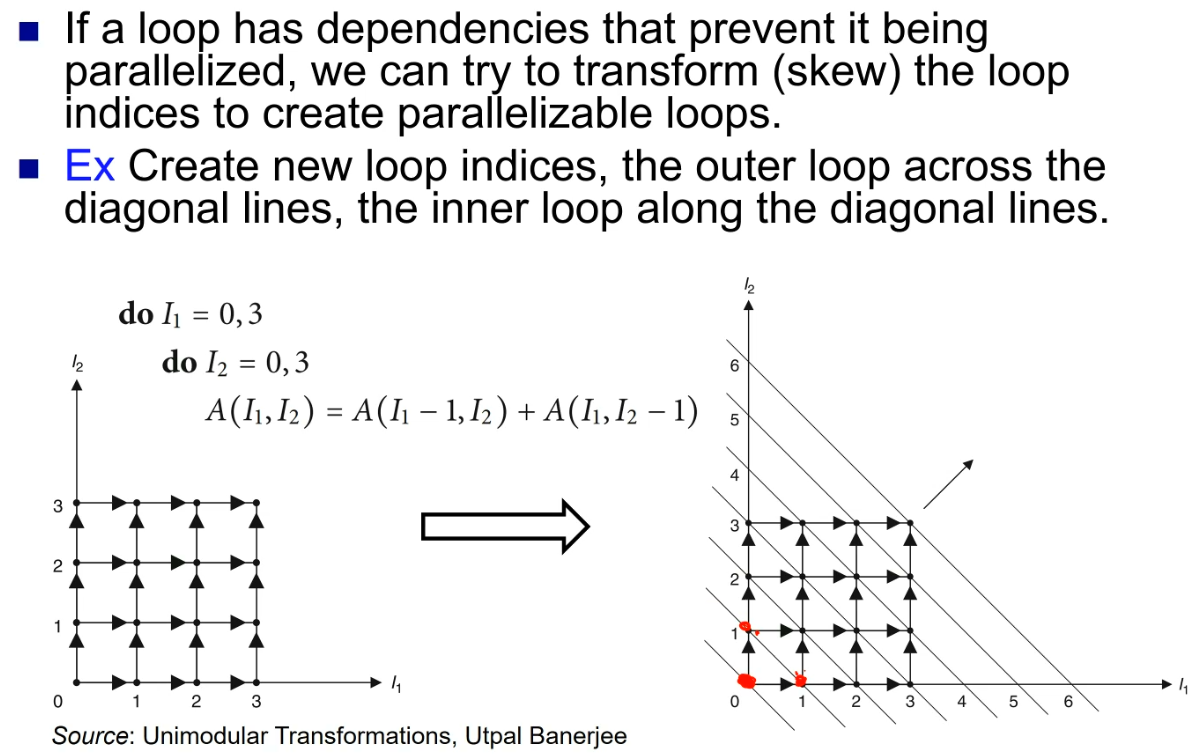
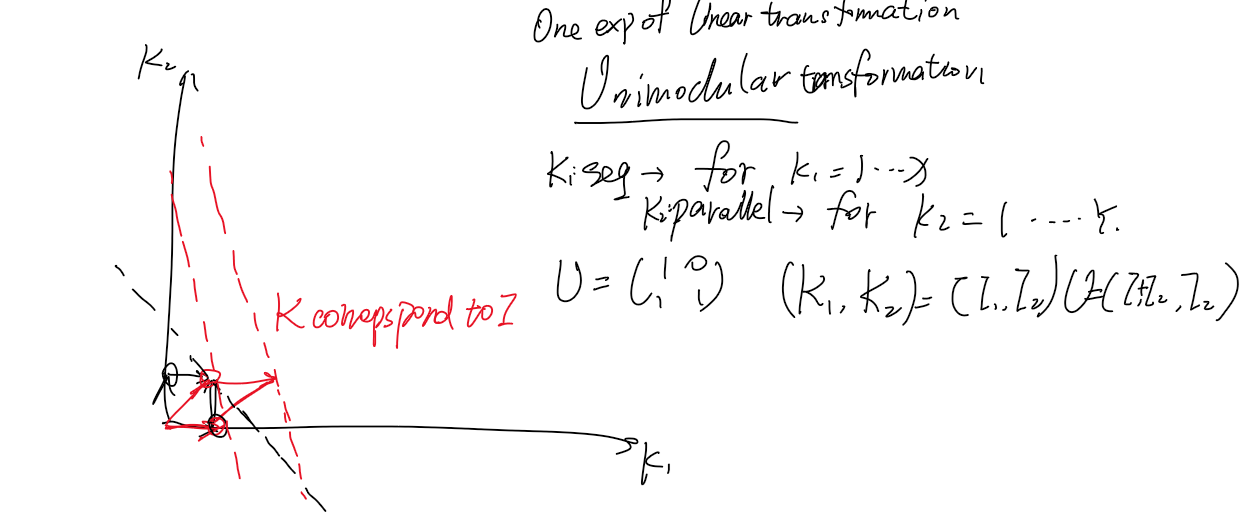
Algorithm analysis