文章目录[隐藏]
The code is at http://victoryang00.xyz:5012/victoryang/sniper_test/tree/lab2.
The lab was to implement the Hash perceptron according to the paper "Dynamic-Branch-Prediction-with-Perceptrons".
The cache implementation is in common/performance_model/branch_predictor.cc
#include "perceptron_branch_predictor.h"
...
else if (type == "perceptron")
{
return new PerceptronBranchPredictor("branch_predictor", core_id);
}
The modification in the cfg
[perf_model/branch_predictor]
type = perceptron # add Perceptron
mispredict_penalty=8 # Reflects just the front-end portion (approx) of the penalty for Interval Simulation
The constructor is passed to the perceptron_branch_predictor.h, we have to maintain the member variable as below:
struct PHT {
bool taken; //jump or not
IntPtr target; //64 history target address.
PHT(bool bt, IntPtr it) : taken(bt), target(it) {}
};//The pattern history table, set like a round linked list to avoid the memory copy
//To store the history result.
SInt32 history_sum;
UInt32 history_bias_index;
std::vector<UInt32> history_indexes;
std::vector<PHT> history_path;
UInt32 history_path_index;
std::vector<PHT> path;
UInt32 path_index;
UInt32 path_length;
UInt32 num_entries;
UInt32 num_bias_entries;//1024
UInt32 weight_bits;
std::vector<std::vector<SInt32>> weights;
std::vector<SInt32> perceptron; //Update the perceptron table to 1024 entries
UInt32 theta; //Threshold, to determine the train is good
SInt64 count; //To store the count
UInt32 block_size; //block sides initialize to perseption
// initialize the branch history register and perceptron table to 0
PerceptronBranchPredictor::PerceptronBranchPredictor(String name, core_id_t core_id)
: BranchPredictor(name, core_id), history_sum(0), history_bias_index(0), history_indexes(64 / 8, 0), history_path(64, PHT(false, 0)), history_path_index(0), path(64, PHT(false, 0)), path_index(0), path_length(64), num_entries(256), num_bias_entries(1024), weight_bits(7), weights(256, std::vector<SInt32>(64, 0)), perceptron(1024, 0), theta(296.64), count(0), block_size(8), coefficients(64, 0)
The prediction method
The Base neral predictor is based on the equation $y=w_{0}+\sum_{i=1}^{n} x_{i} w_{i}$, We have that
// if the prediction is wrong or the weight value is smaller than the threshold THETA,
// then update the weight to train the perceptron
weights = floor(1.93 * blocksize + 14)
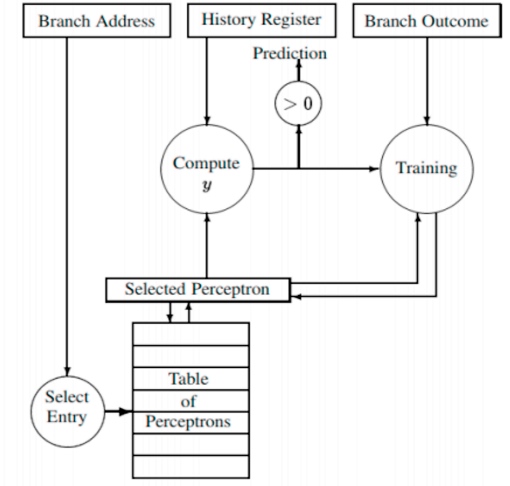
Hashed Perceptron Multiple
- set of branches assigned to same weights
- More than one set of information can be used to hash into the weight table
- Diferent hashing function can be used such as : XOR, Concatenation etc.
- Diferent indices can be assigned to diferent weights
Algorithm
The input is ip, and first come to a computation of (ip >> 4) % num_bias_entries;
This give the seed to the weight table lines:
table of perception will get update to te coefficient*weight and
and weight table will update to weights[index[i]][i*8...(i+1)*8]*coefficients[i*8...(i+1)*8]*h
if the result >0 the prediction is right then jump, or not jump.
Then update the history and insert the round linked list.
bool PerceptronBranchPredictor::predict(IntPtr ip, IntPtr target)
{
double sum = 0;
//hash method
UInt32 bias_index = (ip >> 4) % num_bias_entries;
sum += bias_coefficient * perceptron[bias_index];
history_bias_index = bias_index;
//update the weight
for (UInt32 i = 0; i < path_length; i += block_size)
{
IntPtr z = ip >> 4;
for (UInt32 j = 0; j < block_size; j++)
{
z ^= (path[(path_index - i - j + path_length - 1) % path_length].target >> 4);
}
UInt32 index = z % num_entries;
history_indexes[i / block_size] = index;
for (UInt32 j = 0; j < block_size; j++)
{
SInt32 h = path[(path_index - i - j + path_length - 1) % path_length].taken ? 1 : -1;
sum += h * weights[index][i + j] * coefficients[i + j];
}
}
bool result = ((SInt32)sum) >= 0;
history_sum = (SInt32)sum;
history_path.assign(path.begin(), path.end());
history_path_index = path_index;
path[path_index] = PHT(result, target);
path_index = (path_index + 1) % path_length;
return result;
}
The train process
Algorithm
Input parameters: predicted, actual, ip
auxiliary parameters: history_sum(predicted value), history_bias_index, history_indexes(index). history_path(history), history_path_index(history subscript)
for each bit in parallel
if t=xi then
wi=wi+1
else
wi=wi-1
end if
Realization
for (UInt32 i = 0; i < path_length; i += block_size)
{
index = history_indexes[i / block_size];
for (UInt32 j = 0; j < block_size; j++)
{
bool taken = history_path[(history_path_index - i - j + path_length - 1) % path_length].taken;
if (taken == actual)
{
if (weights[index][i + j] < (1 << weight_bits) - 1)
weights[index][i + j]++;
}
else
{
if (weights[index][i + j] > -(1 << weight_bits))
weights[index][i + j]--;
}
}
}
The result
FFT with Blocking Transpose
1024 Complex Doubles
1 Processors
65536 Cache lines
16 Byte line size
4096 Bytes per page
| pentium_m | perceptron | |
|---|---|---|
| num correct | 63112 | 65612 |
| num incorrect | 4342 | 2112 |
| IPC | 1.36 | 1.37 |
| mpki | 2.71 | 1.39 |
| misprediction rate | 6.436% | 3.118% |
| Elapsed time | 4.46s | 5.23s |
| cycles | 1.2M | 1.2M |
| Instructions | 1.6M | 1.6M |