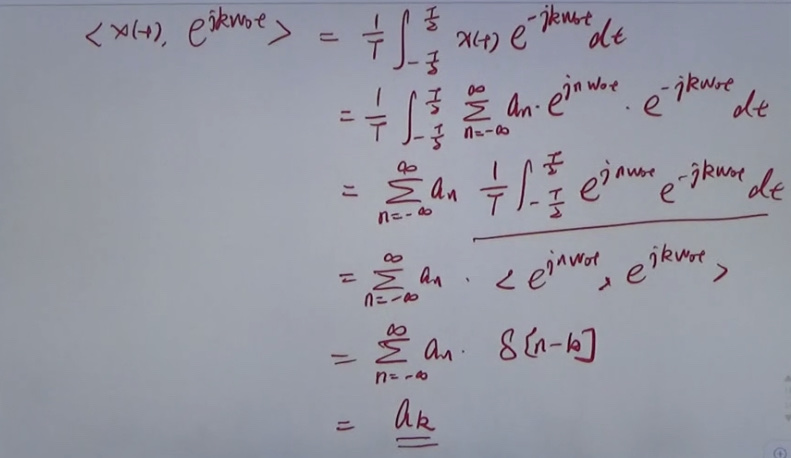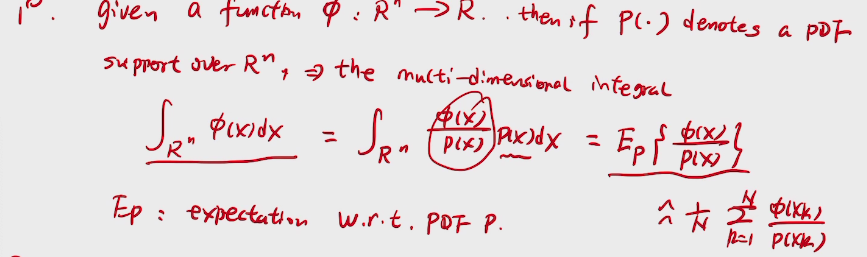[Signal & System] Fourier transform
Definition

Example
- a 3-dim Euclid space \(R^{3} \vec{a}=(1,0,0) \vec{b}=(0,1,0)\vec{c}=(0,0,1)\)
- define n-dim space \(V\)
\(X(t)=\Sigma^{\inf}_{k=-\inf}e^{jk\omega _{0}t}\)
\(S=\{x(t)|x(t)=x(t+t_{0})\forall \}\) \(T_{0}=\frac{2\pi}{\omega_{0}}\)
comment: <2\(T_{0}\)
\(B=\{\phi_{k}t|\phi_{k}(t)=e^{jkw_{0}t} k\in Z\}\) \(B\subset C\)
We have:

The equation above can be deducted then:

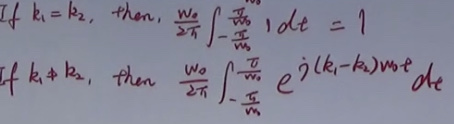

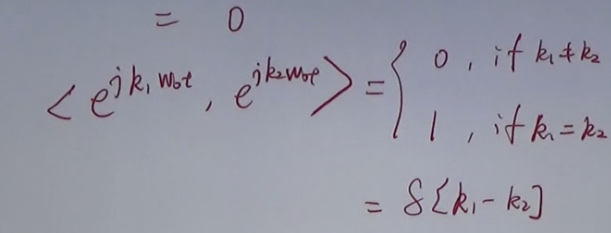
各个弦波都是标准正交积。
Fourier's Idea

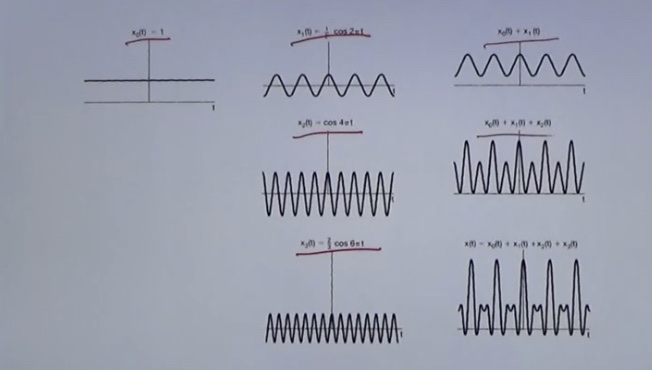
Example

composition in graph
Periodic signals & Fourier Series Expansion cont.

Some simple theory
| time | frequency |
|---|---|
| period | discrete |
| non-period | continuous |
deduction
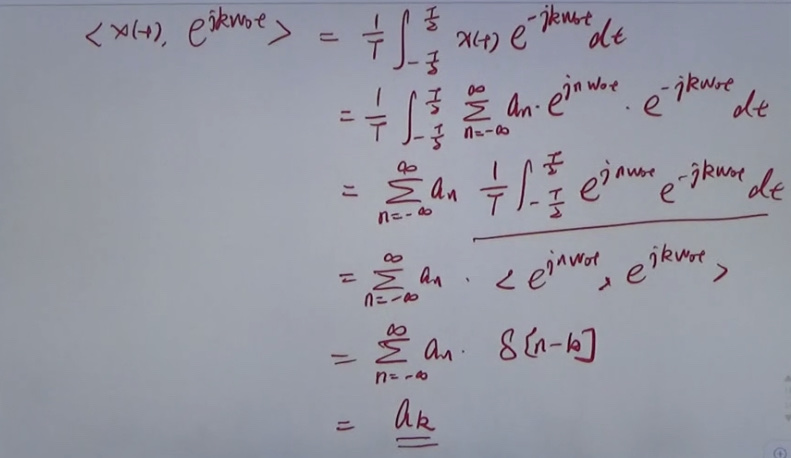
\(a_{k}\) is denoted as Fourier coefficient.
example

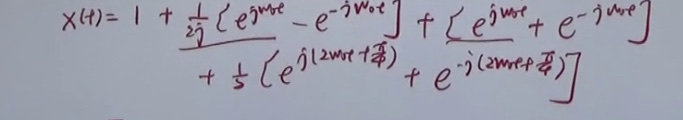
系数\(a_{k}\) -> \(Fourier expression\)
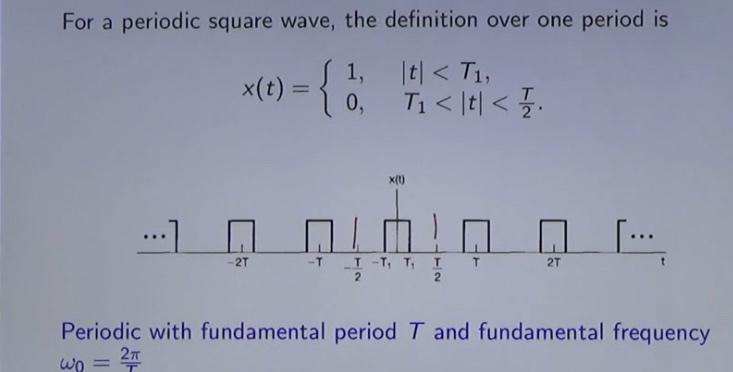

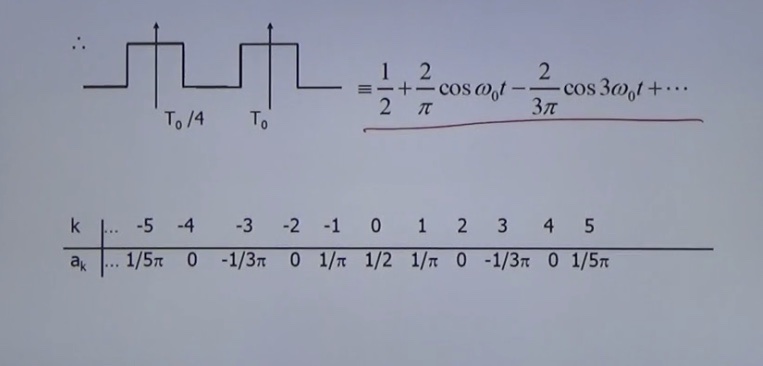
前后均为实系数偶函数
误差

Convergence

决对可积
狄利克雷性质-收敛
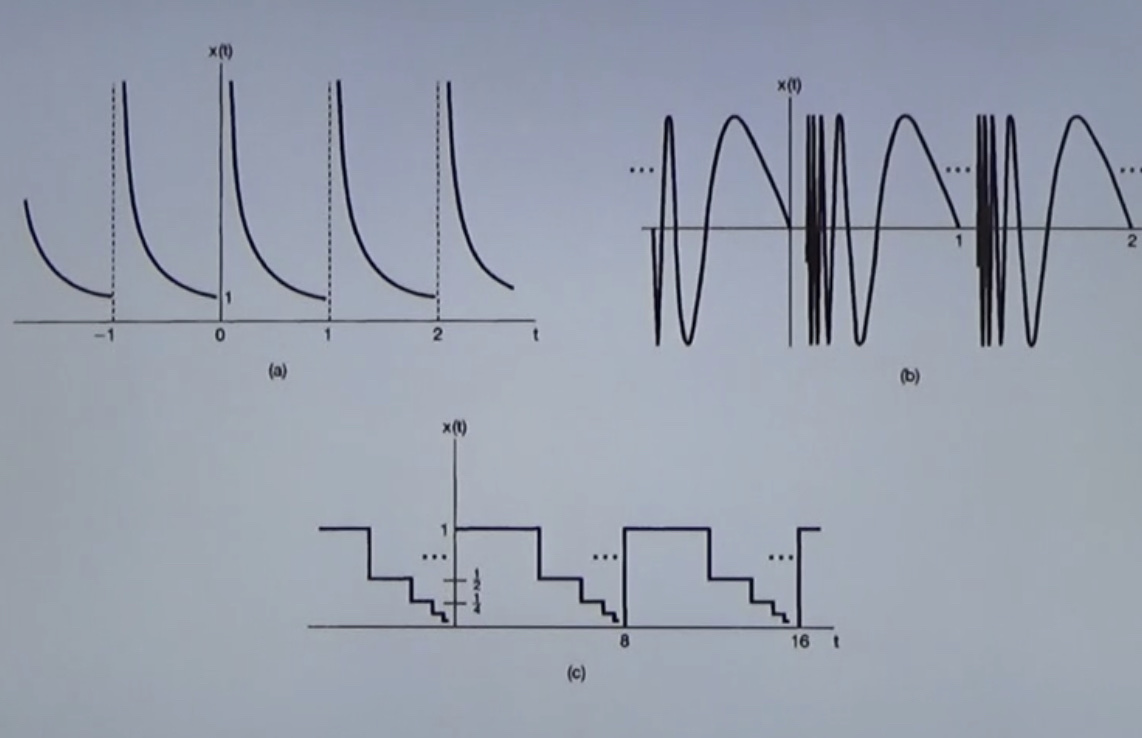
只有第三个满足条件。

条件

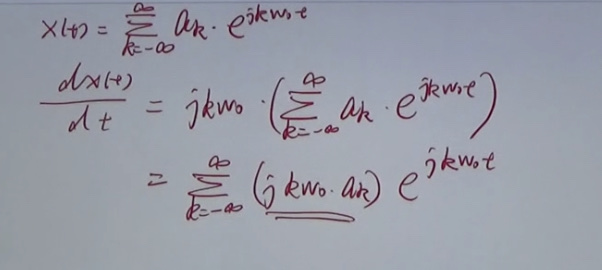
频率域和时间域的 性质等价
性质8

example
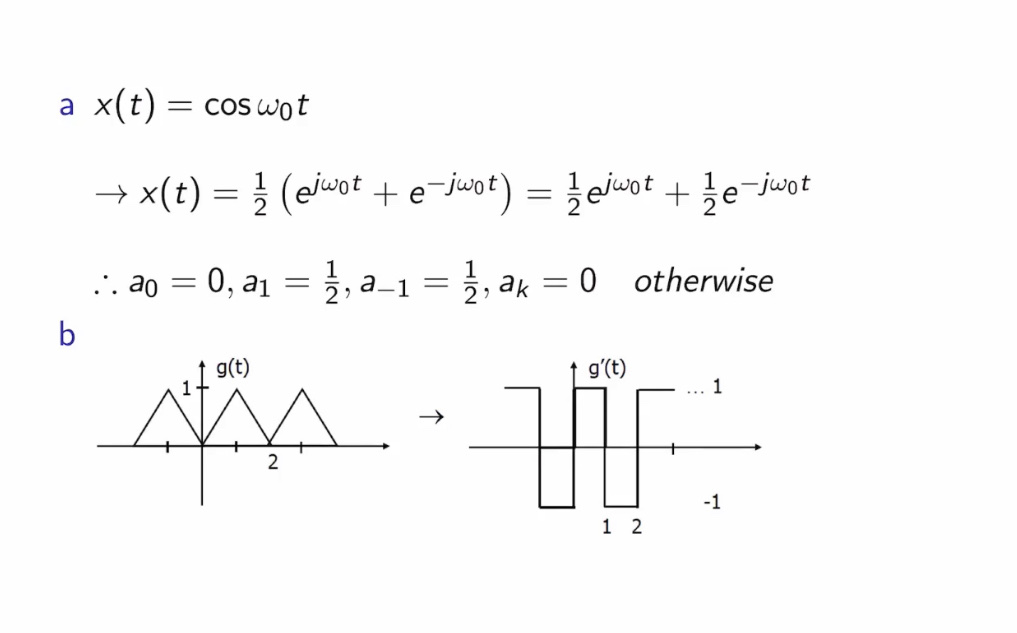
把任何信号变成标准正交积

[Parallel Computing] Architecture
implicit parallelism - pipelinig
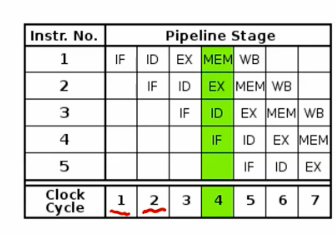
break up one instruction and execute pieces
different unit of cpu utilization
instruction fetch -> decode -> exec -> mem read -> write back
at most 5x with 5 stage pipeline
modern processors has 10-20 stages
if code branches, must guess how to full pipelines.
- branch misprediction requires flushing pipline.
- Typical code every 5 instructions.
so prediction is important
implicit parallelism - Superscalar
- we can have 2 fetch unit each clock

((i)has fewer data dependencies (iii)should be rescheduled.)
e.g.
1000 1004 1008 100C
--o---o---o---o
-- |---/ ---|---/
---R1 ----- R2
----|-----/ - execution must respect data dependencies.
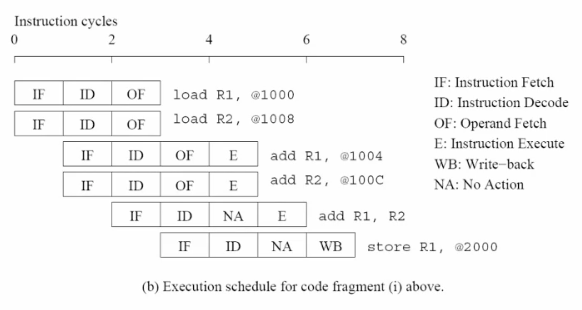
To deal with data race, Use DAG to label them.
Look ahead using CA to reorder the instruction set.
## implicit parallelism - VLIW(compile time)

memory performance
latency & bandwidth
speed & lanes
memory hierarchy
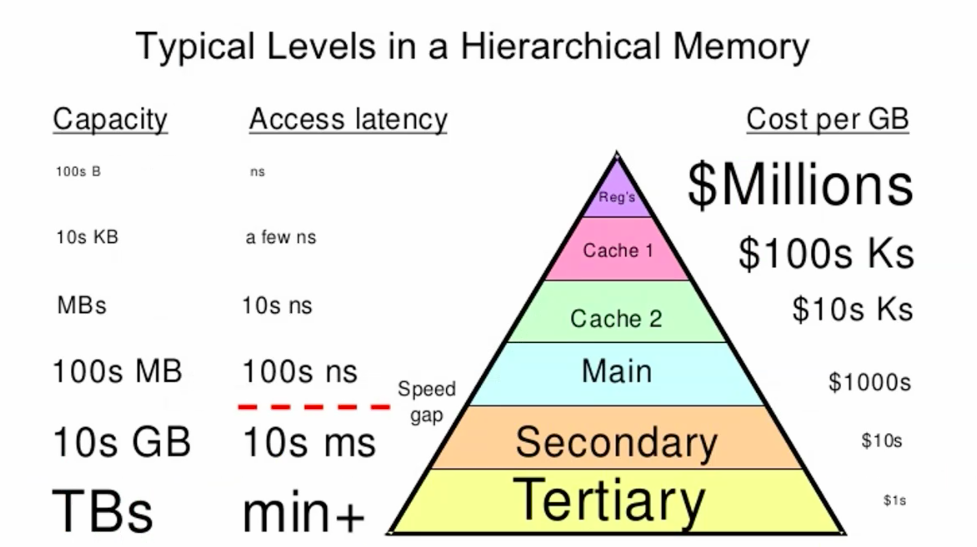
caching
locality
Temporal locality - small set of data accessed repeatedly
spacial locality - nearby pieces of data accessed together
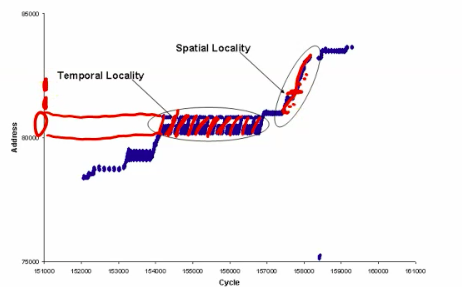
e.g.
Matrix Multiplications have both temporal locality and spatial locality.
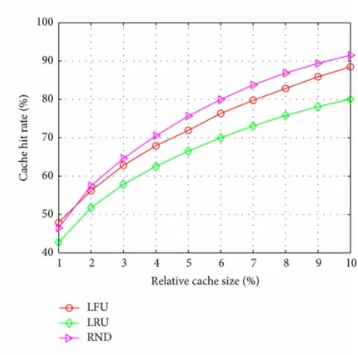
performance
cache hit rate is the proportion of data accesses serviced from the cache.
e.g.

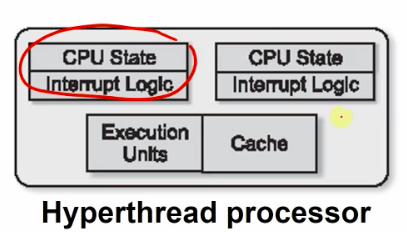
processor architectures
- a multiprocessor contains several cores communicating through memory.
- a multicore has several cores on a single die.
- each core is a complete processor, but runs simultaneously.
- they share L2/L3 cache.
- cheap to replicate CPU state.(registers, program counter, stack) (SMT)
GPGPU
1000+ core stream simultaneously.
Flynn's taxonomy
- SISD conventional sequential processor.
- SIMD single control unit for multiple processing unit
- MISD uncommon
- MIMD Distributed systems
SIMD
- control unit fetches single instruction and broadcast it to processing units.
- PEs each apply instruction to its own data item in synchrony.
- e.g. adding two arrays.
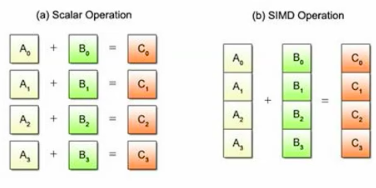
- very popular today.
- dgemm, graphics and video, ML
- cheap to implement, don't duplicate hardware for fetch.
- Used in GPU(SIMT), avx, phi
- 100s bits lanes -> 4-32 lanes
- e.g. adding two arrays.
Instruction divergence
SIMD processors can perform different instructions.
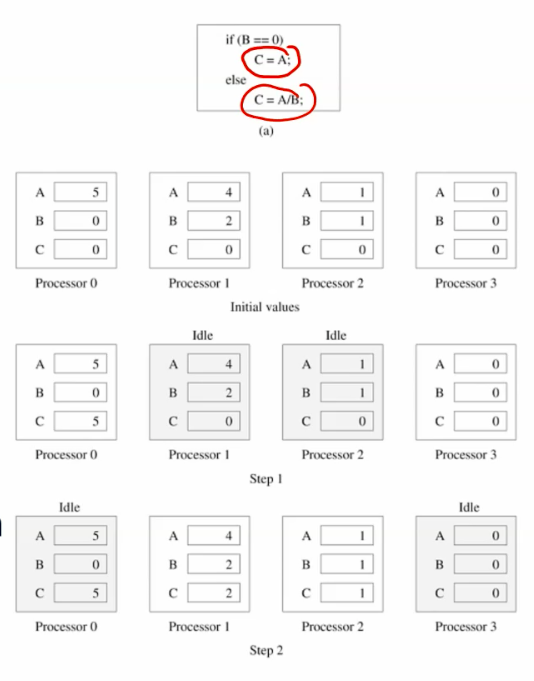
Interconnection networks
- built using links and switches
- links are fixed connection between 2 processors.
- switch connect set of processors on input ports with processors on output ports
- static vs. dynamic
- quadratic needed
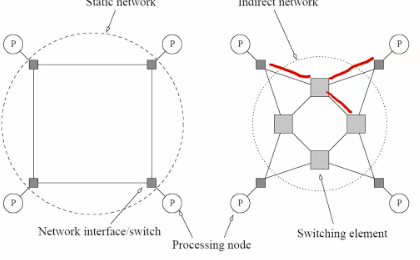
shared memory architecture
all processors shared the same mems-pace.
Pros: easy to write program
Cons: limited scalability.
UMA vs. NUMA
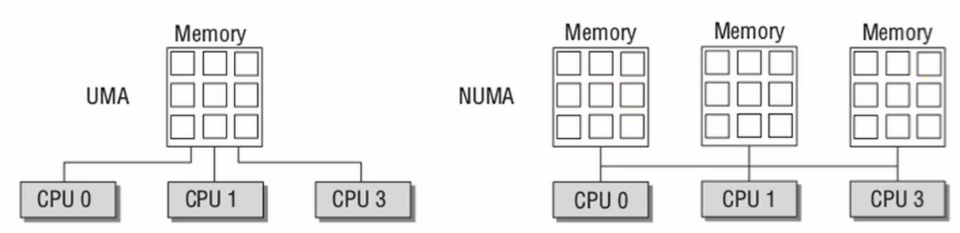
Distributed memory architecture
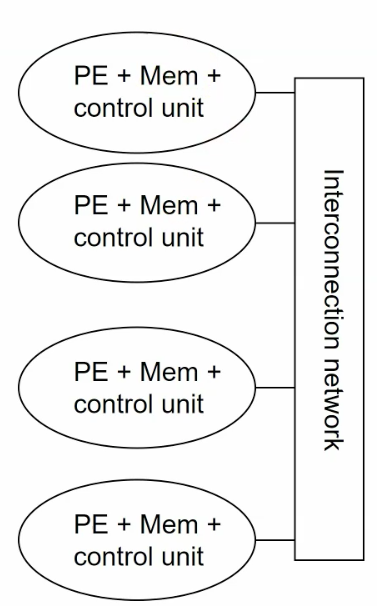
combination of shared memory and non-shared memory.
Network of workstation(NOW)
connect workstations with networking.
e.g. Beowulf
Bus architecture.
all processors use mem on the same bus.
the bandwidth is the bottlenech.
Crossbar architecture.
switched network for higher end shared memory system.
allow all processors to communicate with all mem modules simultaneously. -nonblocking
Higher bandwidth
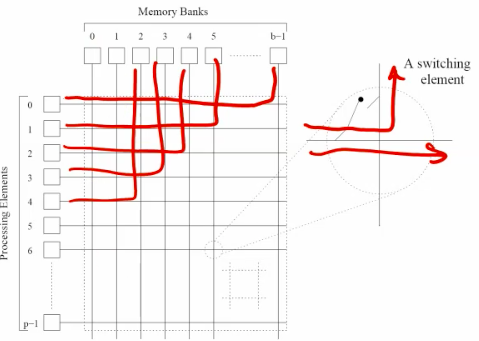
topology
multihop networks.
The combination of the bus and cross bar. flexibility between bandwidth and scalability.
feature:
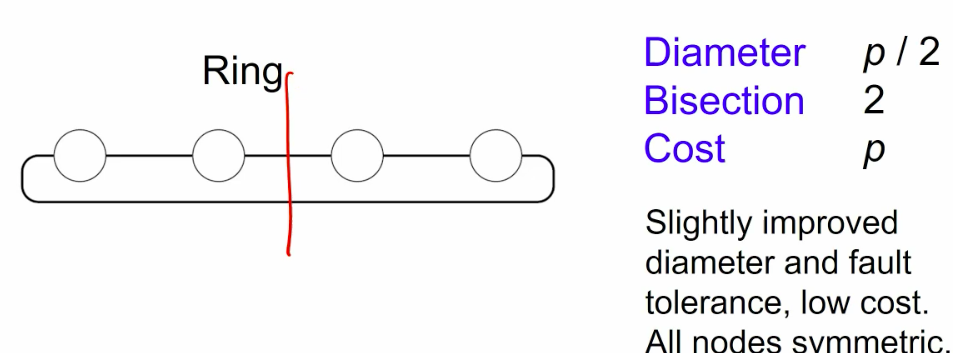
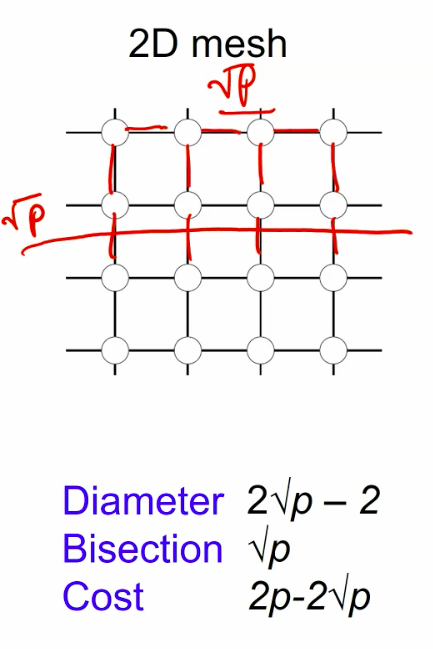
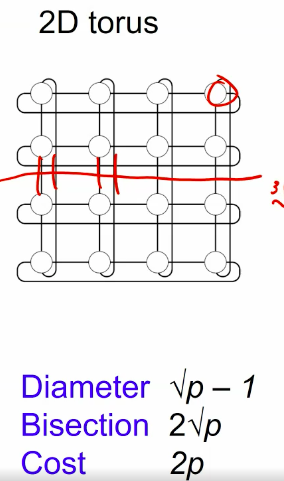
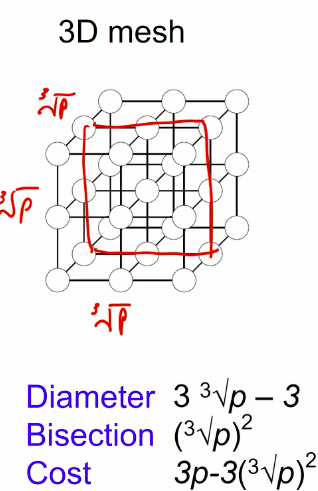
- Diameter
- Distance between farthest pair of processors.
- Gives worst case latency.
- Bisection width. - fault tolerence
- Minimum number of links to cut to partition the network into 3 equal halves.
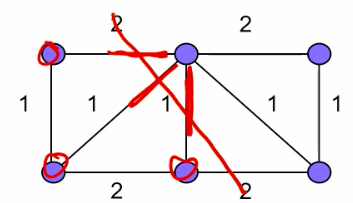
- Indicates bottlenecks.
- links out bandwidth.
- Minimum number of links to cut to partition the network into 3 equal halves.
- cost
- the number of links.
1d topologies
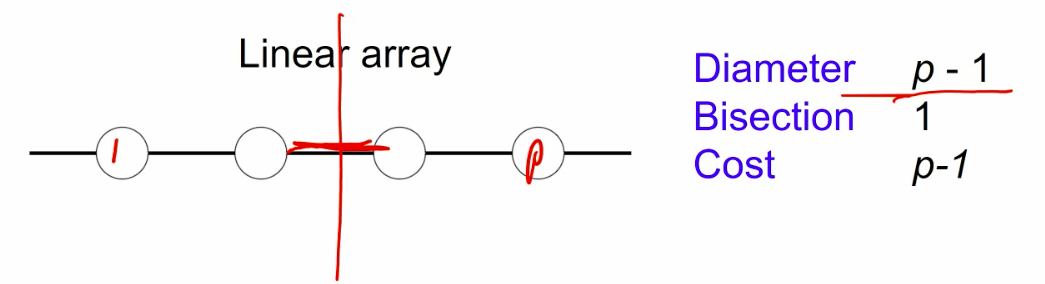
meshes and tori
hypercube
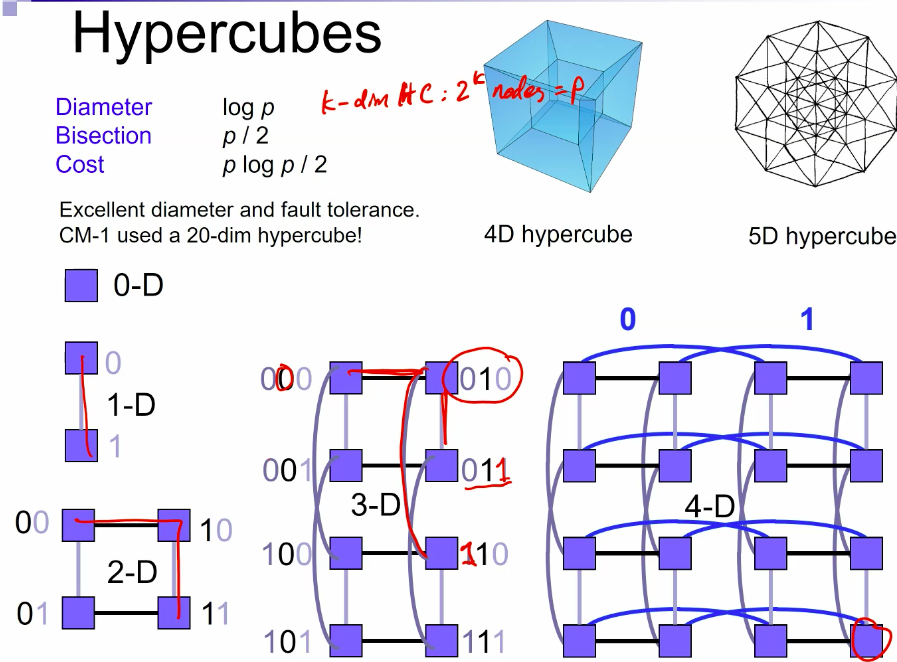
advantage
- good algorithm to calculate the path(only change the number of different bit)
- Bisection can always be \(\frac{P}{2}\) so there's little bottleneck
- nodes do not have hierarchy (v.s. fat tree)
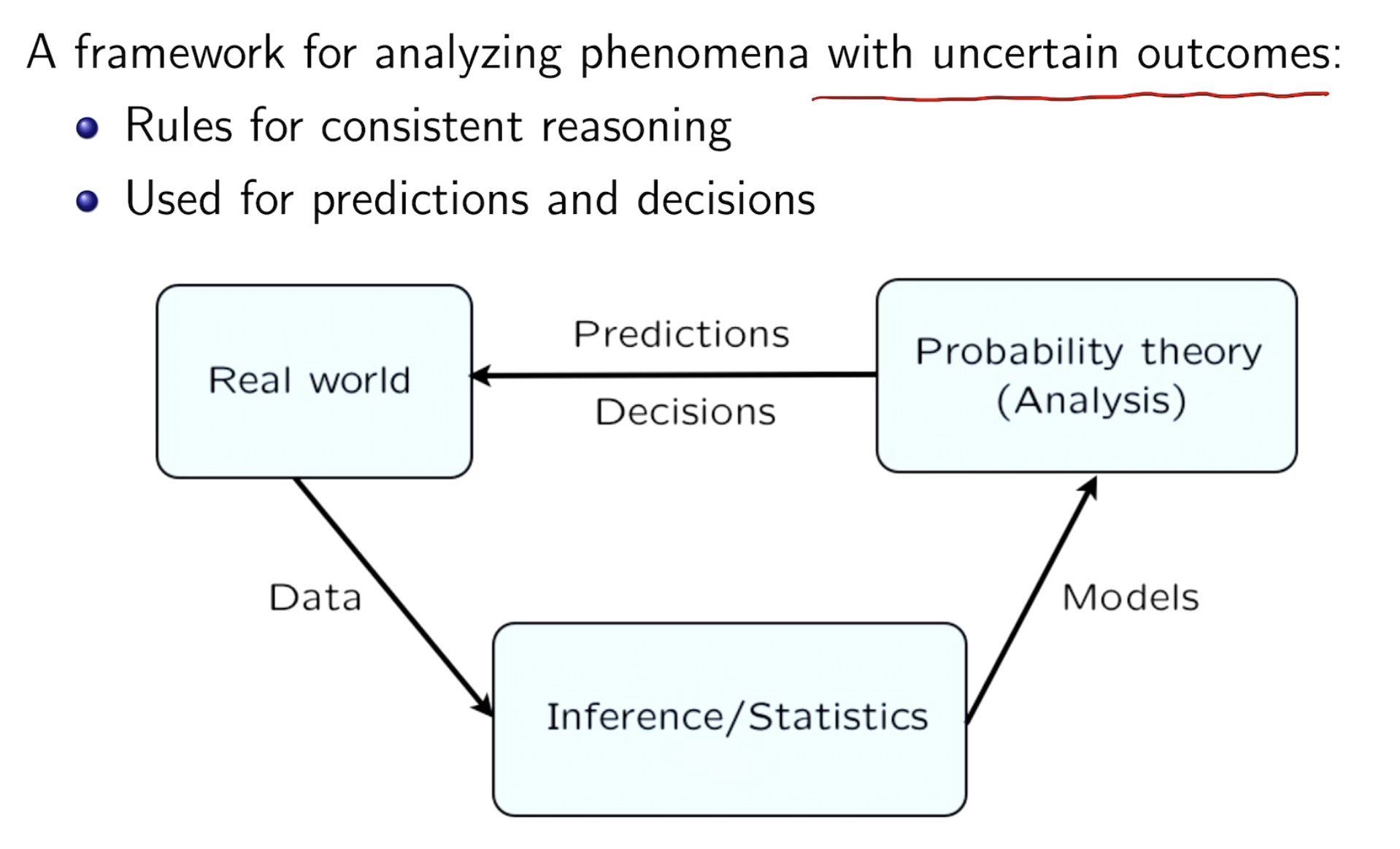
[RL] Probability Review
Basics
The set
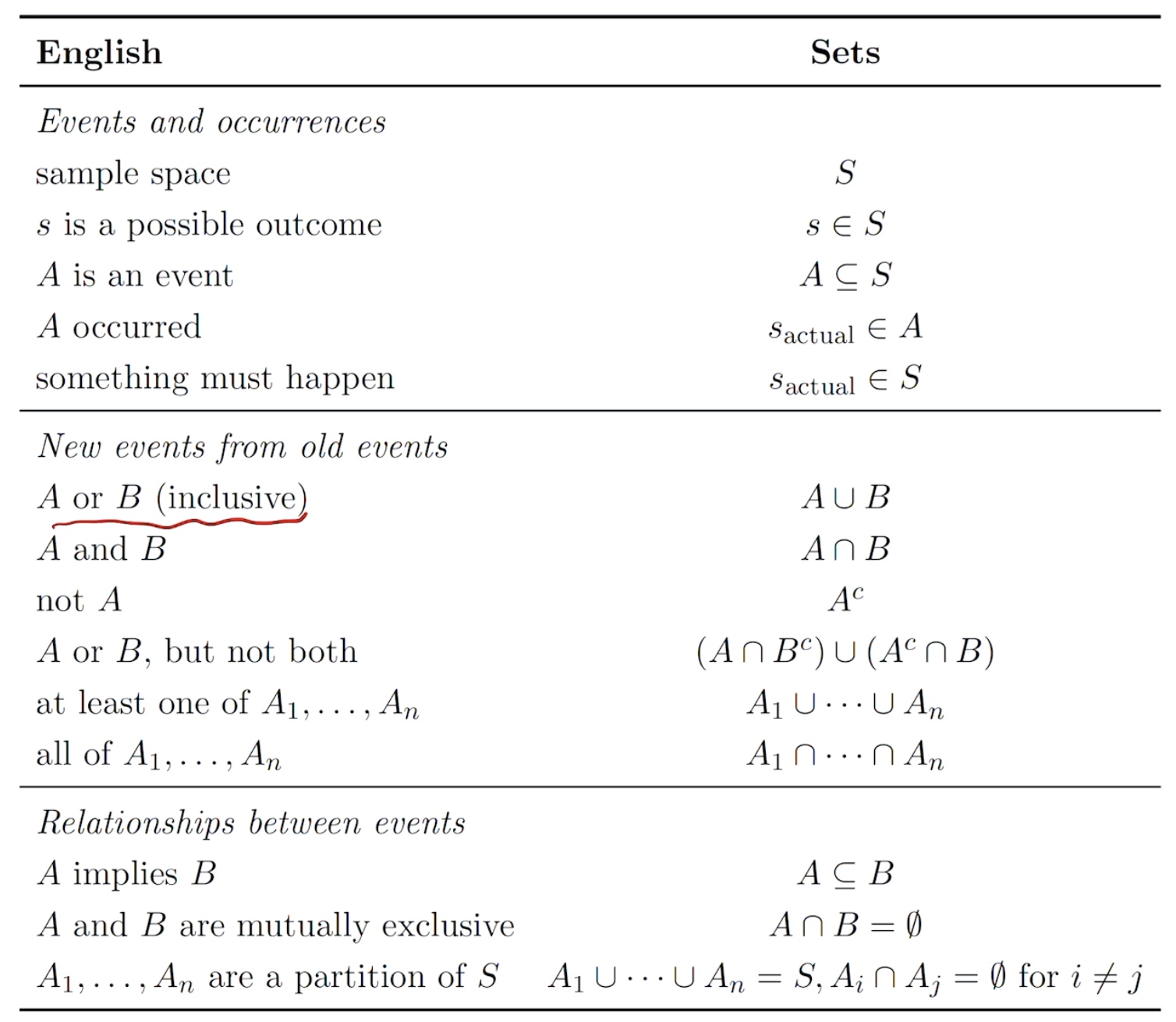
general definition of Probability
样本空间
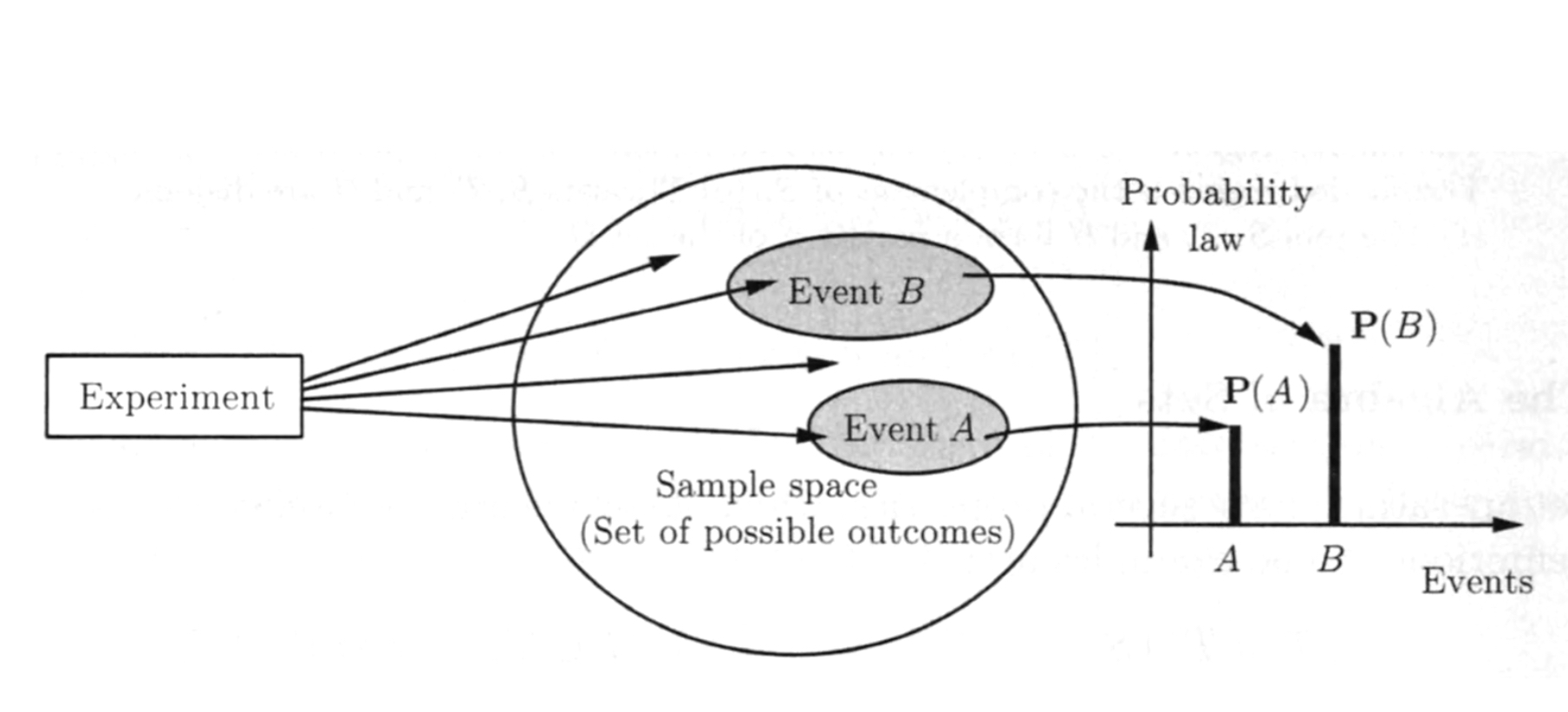
概率的物理意义
frequentist view: a long-run frequency over a large number of repetitions of an experiment.
Bayesian view: a degree of belief about the event in question.
We can assign probabilities to hypotheses like "candidate will win the election" or "the defendant is guilty"can't be repeated.
Markov & Monta Carlo + computing power + algorithm thrives the Bayesian view.
role
条件概率
所有事情都有条件,条件就会产生概率
e.g. Conditioning -> DIVIDE & CONCUER -> recursively apply to multi-stage problem.
P(A|B) = \(\frac{P(A\ and\ B)}{P(B)}\)
chain rules
有利于分布式计算
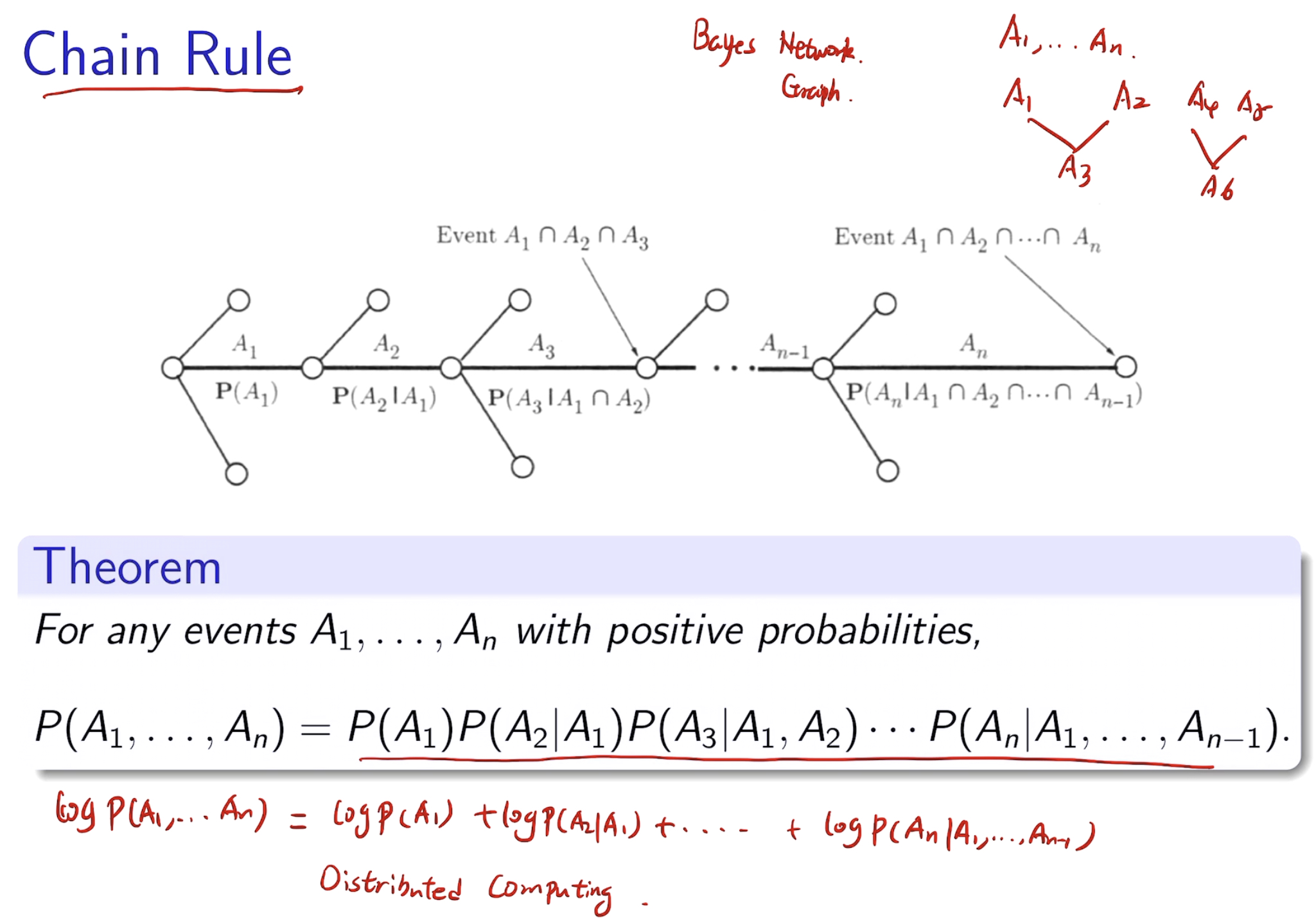
Inference & Bayes' Rules
概率分布和极限定理
PDF 概率密度函数
混合型

valid PDF
- non negative \(f(x)\geq0\)
- integral to 1:
\(\int^{\infty}_{-\infty}f(x)dx=1\)
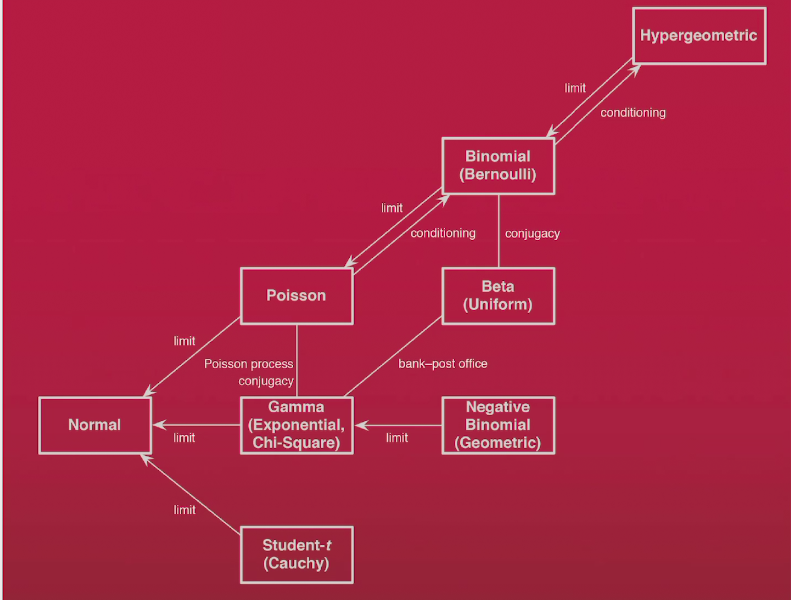
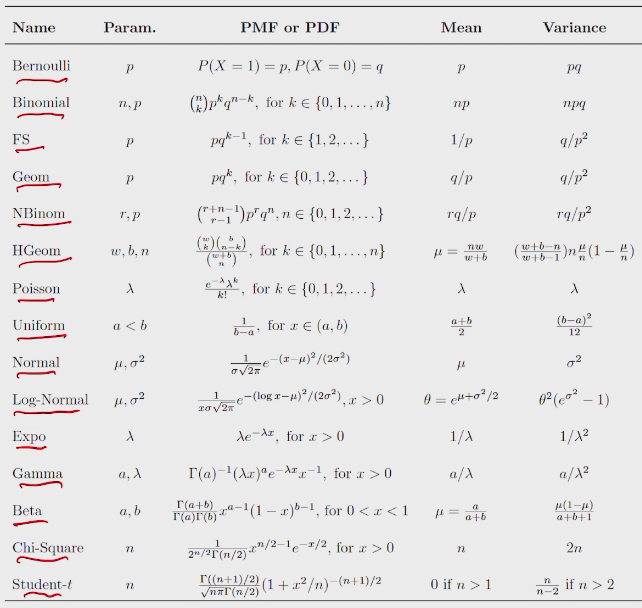
probability distribution
summary of probability distribution
三种距离衡量 in ML, DL, AI
全变量距离
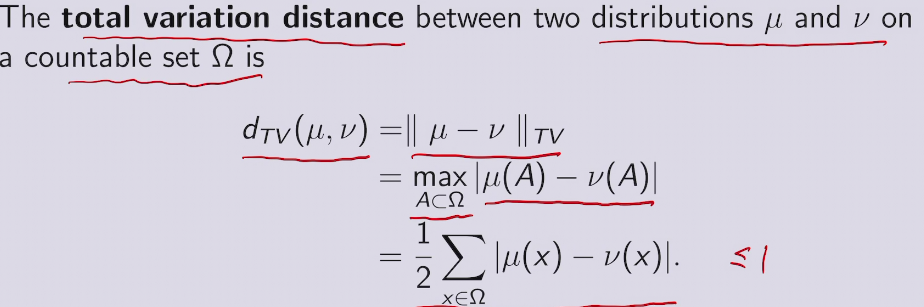
usually in GAN
小数定理(稀疏事件) in poisson
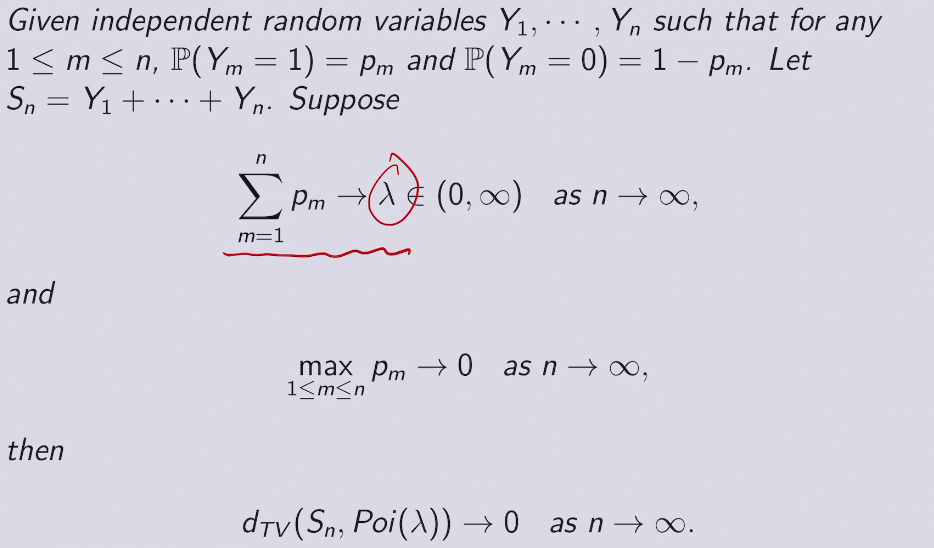
去食堂吃饭人数可以用柏松分布来描述
Sample mean
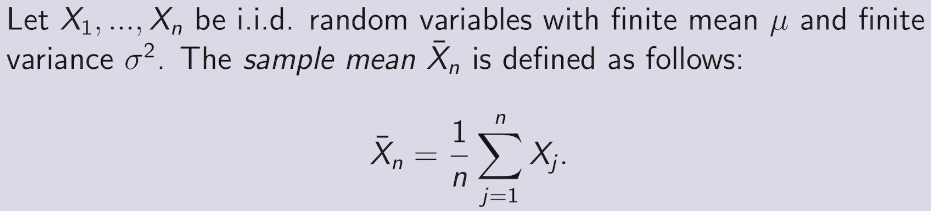
强大数定理SLLN

收敛到真正的概率值以概率为一收敛
弱大数定理WLLN
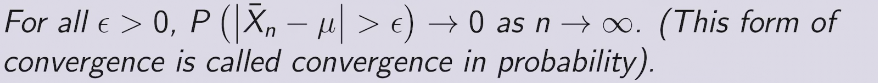
以概率收敛
中心极限定理

Generating function
- PGF - Z
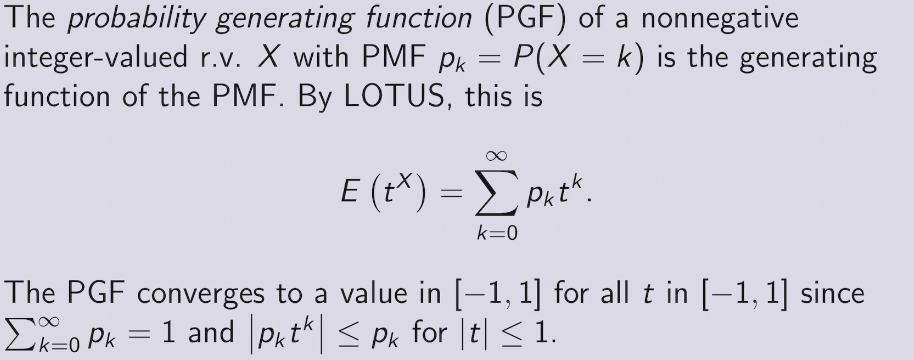
- MGF - Laplace

- CF - 傅立叶
APPLICATION
- branching process
- bridge complex and probability
- play a role in large deviation theory
## Multi variables.
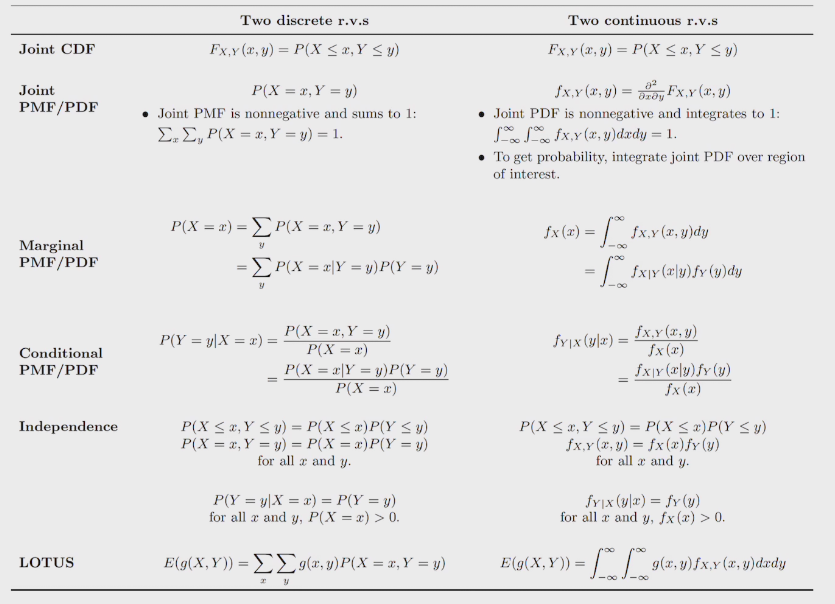
joint distribution provides complete information about how multiple r.v. interact in high-dimensional space

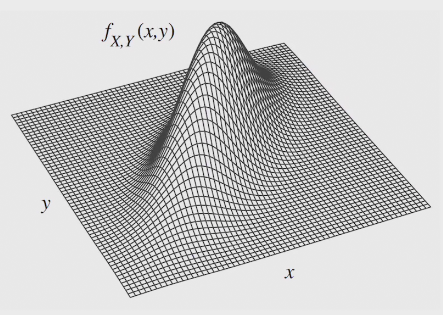
joint CDF &PDF
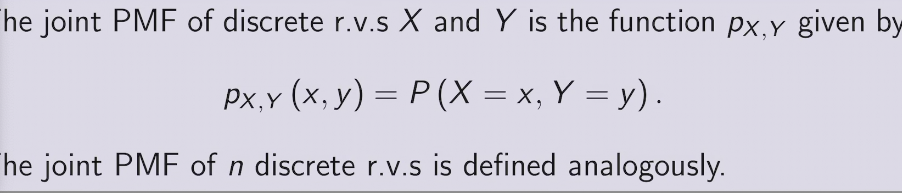
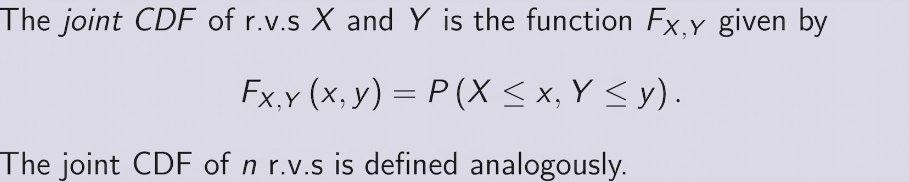
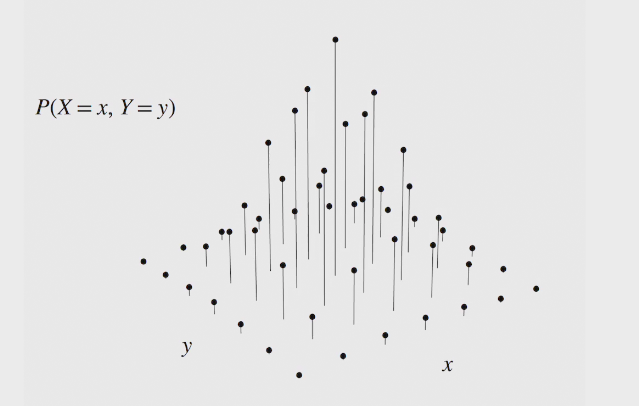
marginal PMF
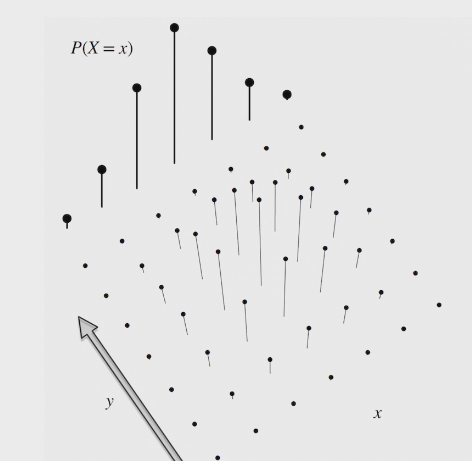
conditional PMF
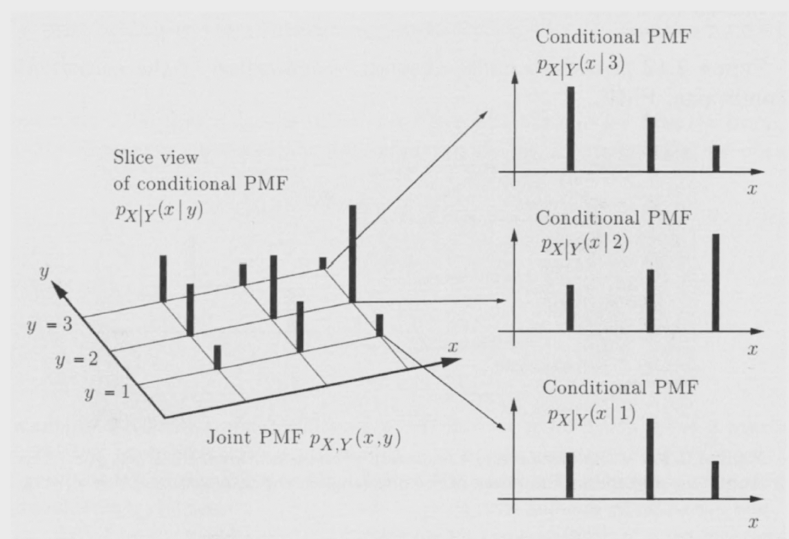
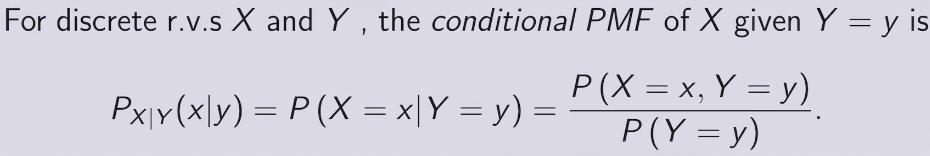
joint PDF
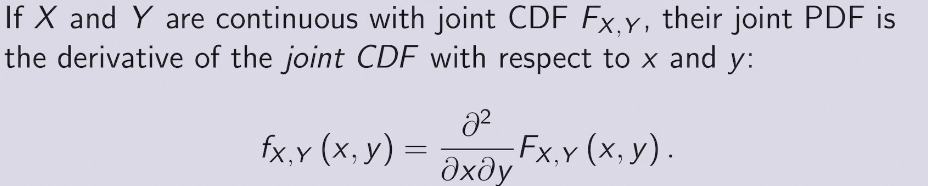
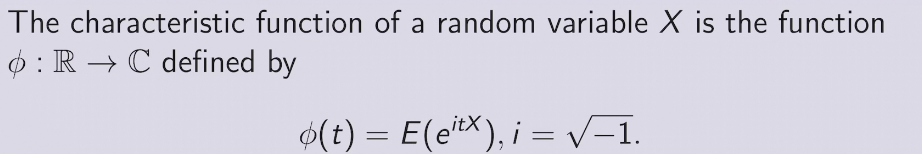
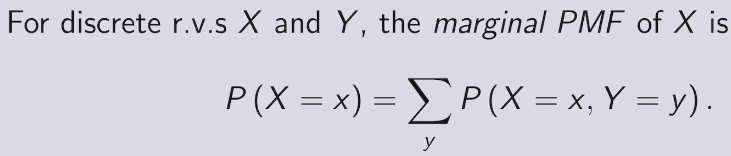
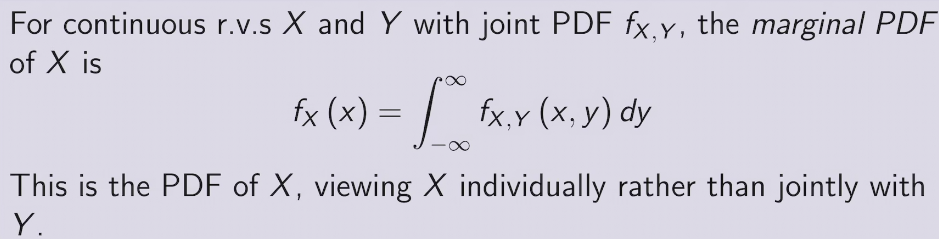
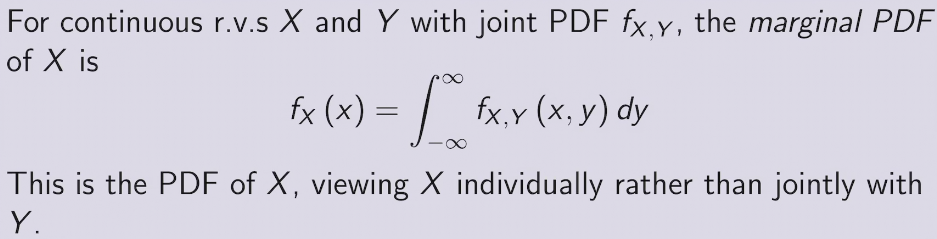
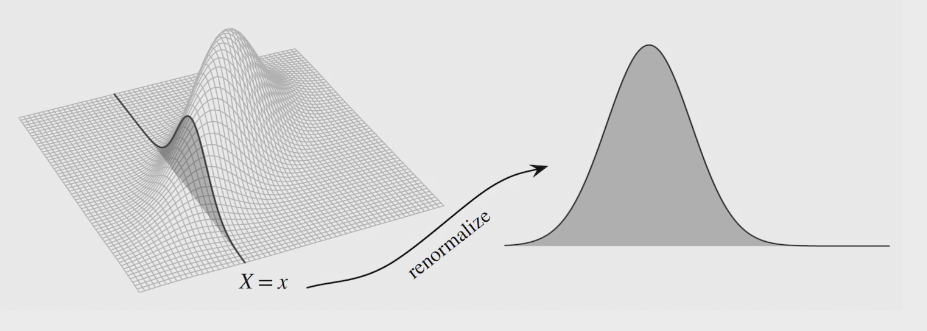
techniques

general Bayes' Rules.
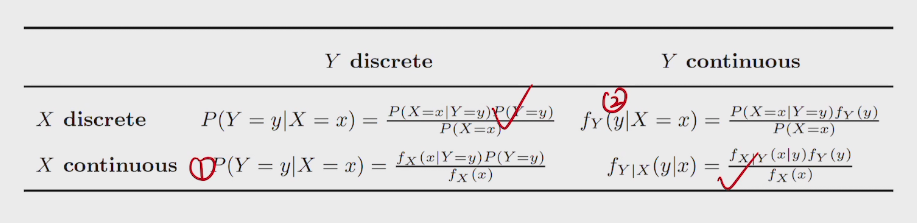
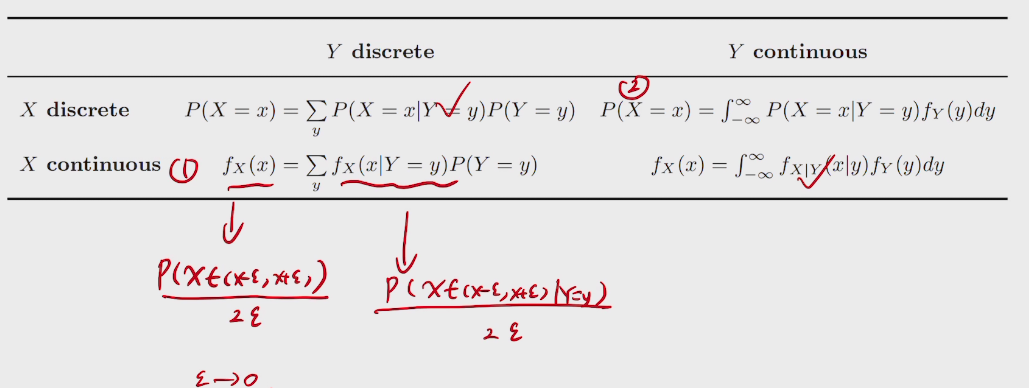
general LOTP
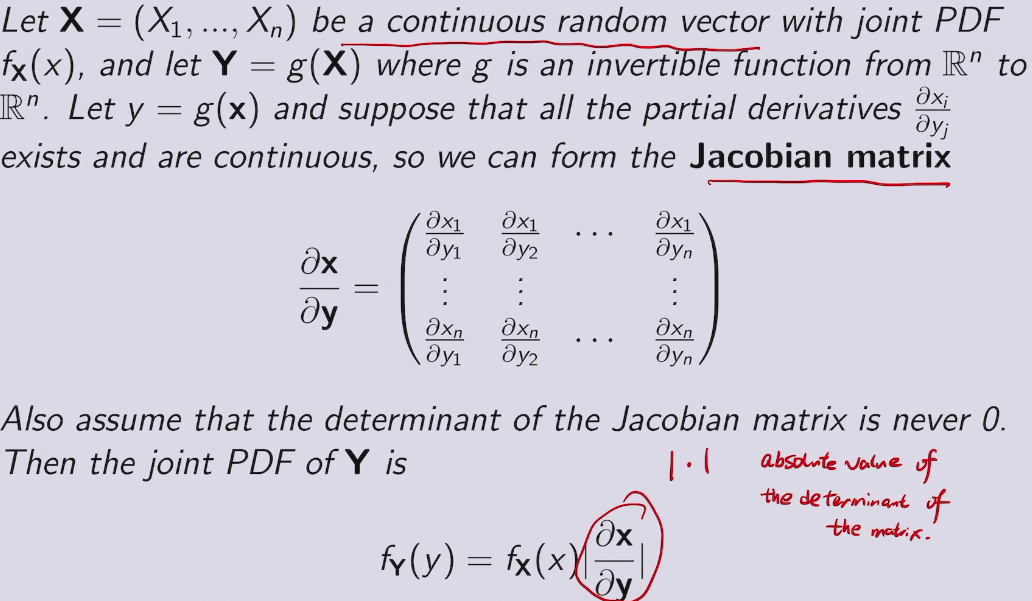
change of variables
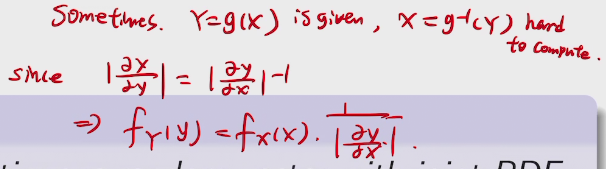
summary
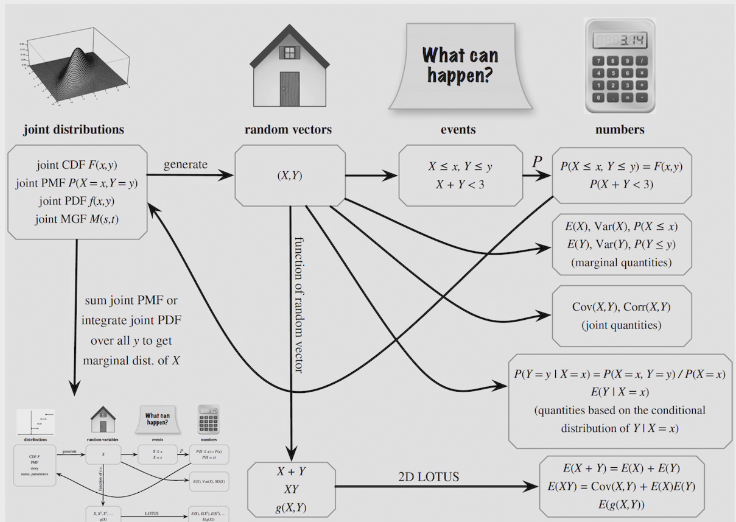
Order Statistics
CDF of order statistic
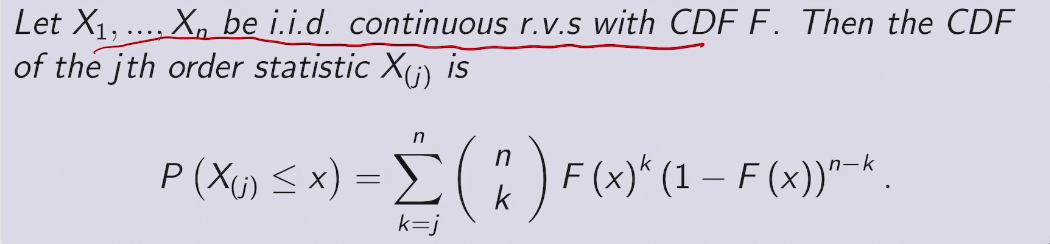
proof
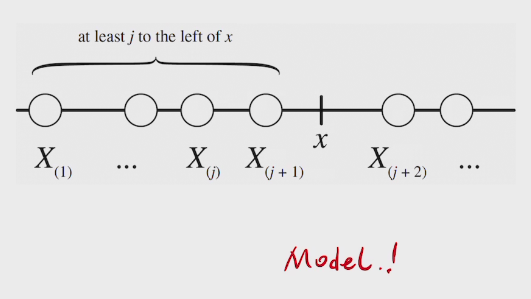
PDF of Order Statostic

two methods to find PDF
- CDF -differentiate> PDF (ugly)
- PDF*dx

###proof
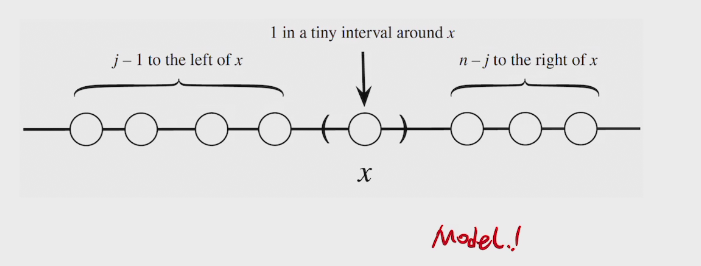
## joint PDF
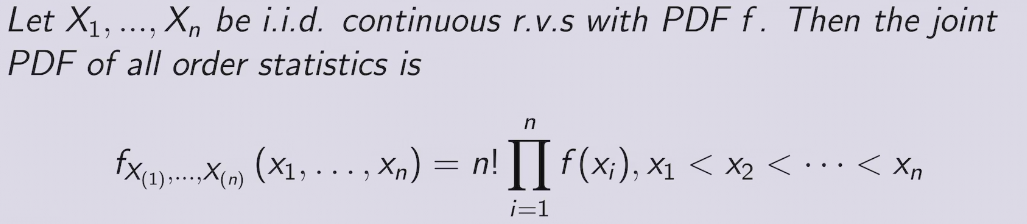
e.g. order statistics of Uniforms
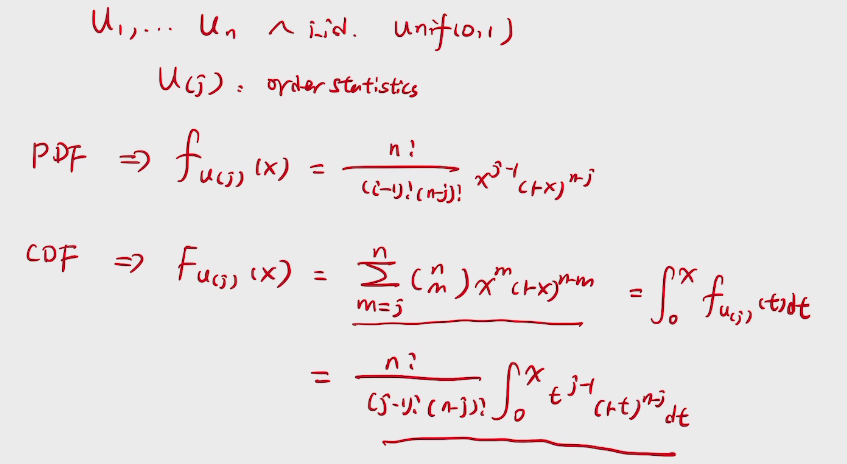
story:beta-Binomial Conjugacy
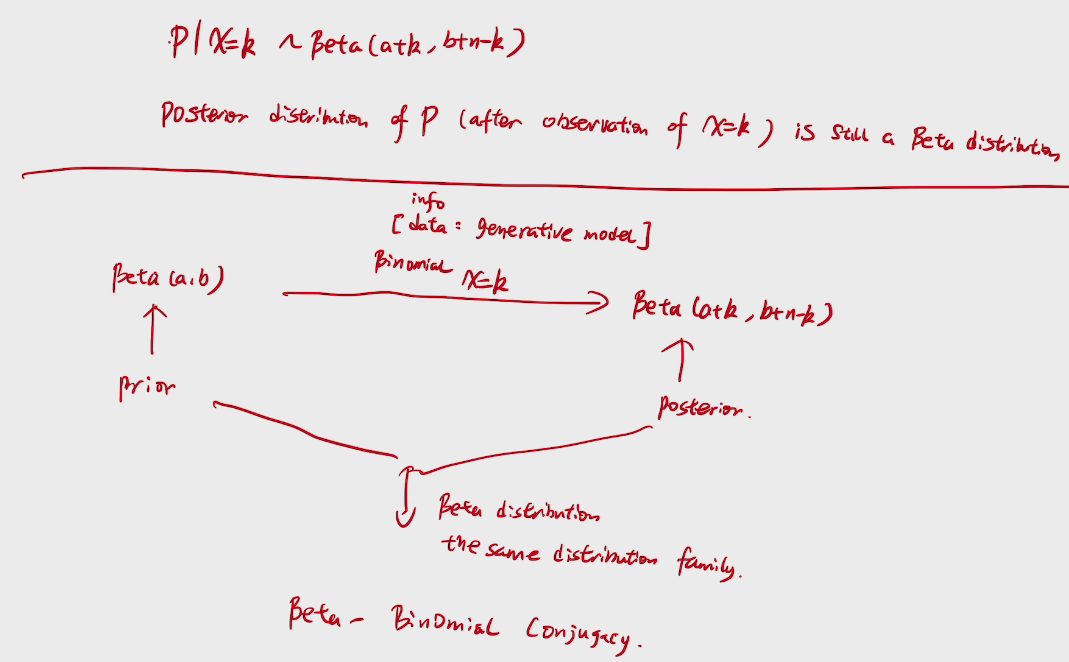

Mean vs Bayes'

deduction

e.g. 拉普拉斯问题
来自大名鼎鼎的拉普拉斯的问题,若给定太阳每天都升起的历史记录,则太阳明天仍然能升起的概率是多少?
拉普拉斯自己的解法:
假定太阳升起这一事件服从一个未知参数A的伯努利过程,且A是[0,1]内均匀分布,则利用已给定的历史数据,太阳明天能升起这一事件的后验概率为
\(P(Xn+1|Xn=1,Xn-1=1,...,X1=1)=\frac{P(Xn+1,Xn=1,Xn-1=1,...,X1=1)}{P(Xn=1,Xn-1=1,...,X1=1)}\)=An+1 在[0,1]内对A的积分/An 在[0,1]内对A的积分=\(\frac{n+1}{n+2}\),即已知太阳从第1天到第n天都能升起,第n+1天能升起的概率接近于1.
Monte carlo
importance sampling

reduce the 方差
importance sampling
example

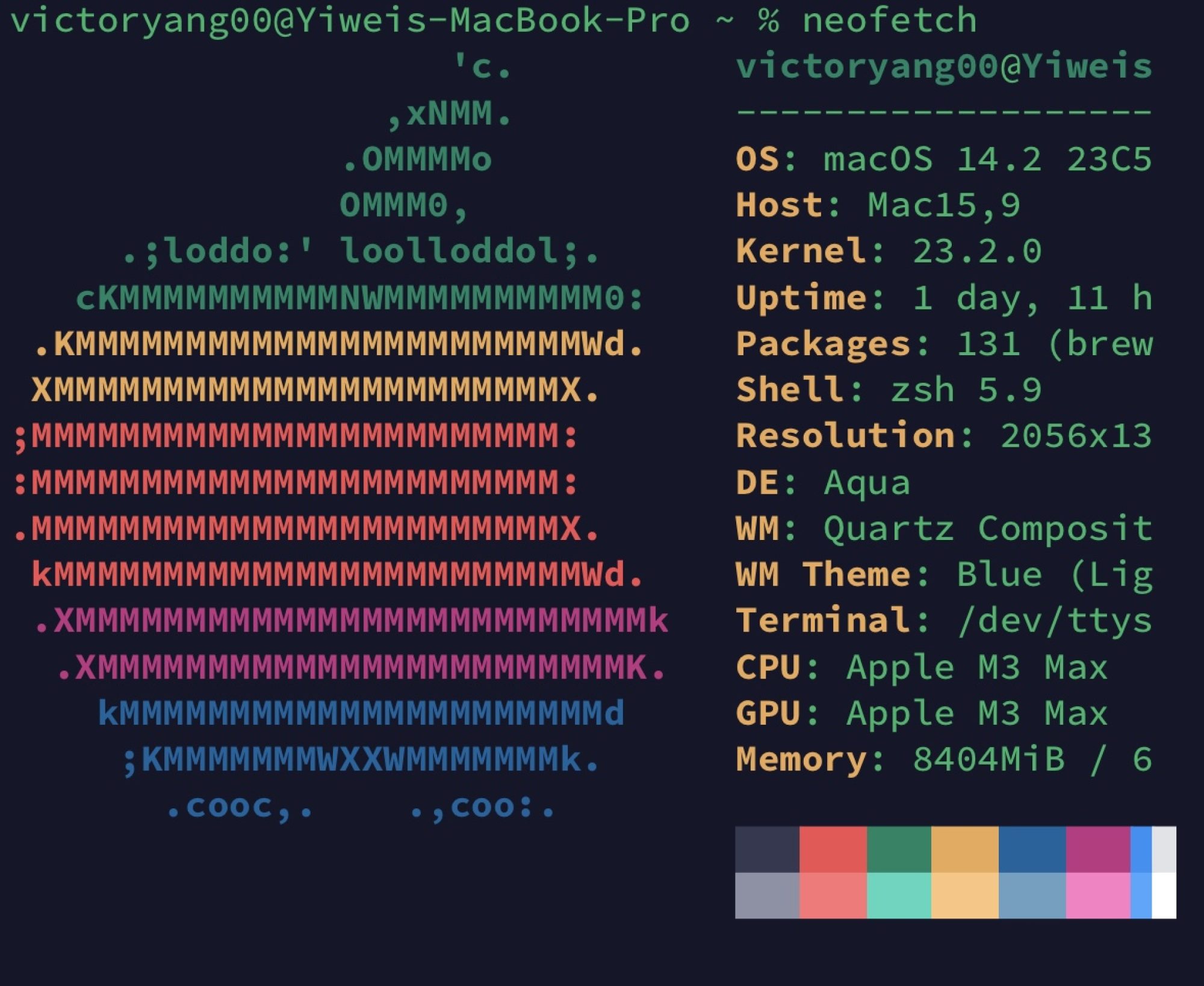
[Computer Architecture] Numbers Notes
big IDEAs
- Abstraction
- Moore's Law
- Principle of Locality/Memory Hierarchy
- Parallelism
- Performance Measurement and Improvement
- Dependability VIA Redundancy
old conventional wisdom
Moore's Law t+ Dennard Scaling = faster, cheaper, low-power
signed &unsigned Intergers
unsigned
e.g. for unsigned int: adresses
0000 0000 0000 0001\(_{two}\) = \(1_{ten}\)
0111 1111 1111 1111\(_{two}\) = \(2^{11}-1\ _{ten}\)
signed
e.g. for signed int: int x,y,z;
1000 0000 0000 0000\(_{two}\) = \(-2^{11}\ _{ten}\)
main idea
want \(\frac{1}{2}\) of the int >=0, \(\frac{1}{2}\) of the int <0
two complement
basic ideas
for 3\(_{ten}\)=0011\(_{two}\)
for 10000\(_{two}\)-0011\(_{two}\)=1\(_{two}\)+1111\(_{two}\)-0011\(_{two}\)=1101\(_{two}\)
more e.g.
Assume for simplicity 4 bit width, -8 to +7
represented
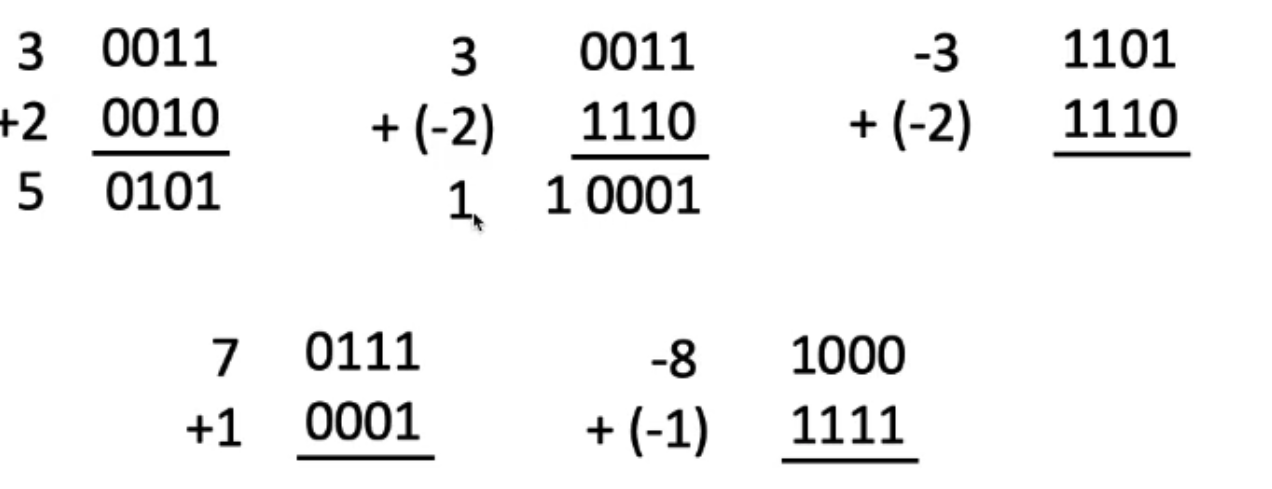
There's an overflow here
Overflow when magnitude of result too big to fit into result representation
Carry in = carry form less significant bits
Carry out = carry to more significant bits
take care of the MSB(Most significant bits)
to detect overflow is to check whether carry in = carry out in the MSB
summary
test of vega sgemm
0.841471 0.540302 0 16384 16384 640 656 656 16400 0.6 0.6
9 3 0 512 512 256 512 256 512 1.4013e-44 2
0.841471 0.540302 0 512 512 256 272 272 528 1.4013e-44 2
cout<<A[1]<<" "<<B[1]<<" "<<C[1]<<" " <<m << " "<<n<<" "<<k<<" "<<lda<<" "<<ldb<<" "<<ldc<<" "<<alpha[1]<<" "<<beta[1]<<endl;
[Parallel Computing] Intro
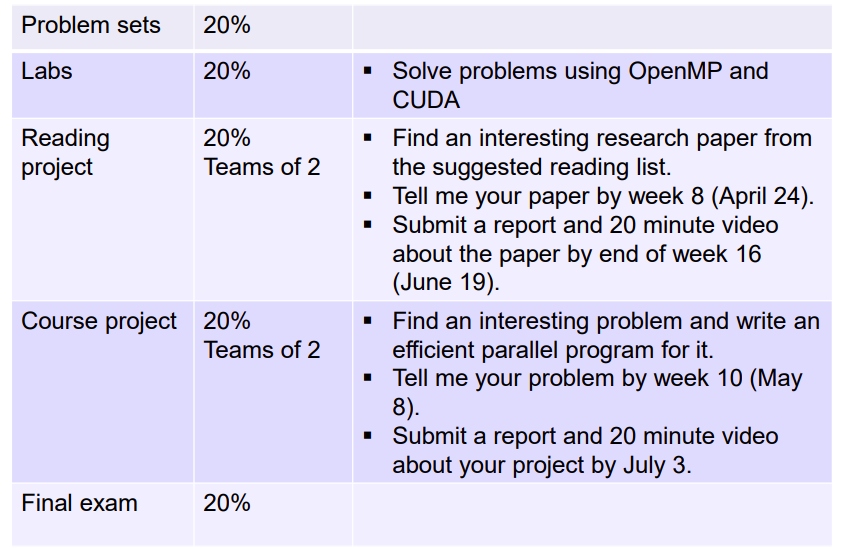
Administrivia
curent ddl

score complement
what and why
applications
- Fluid dynamics
- DNA & drug
- Quantum / atomic simulation, cosmological
challenges
- Harnessing power of masses
- Communication
- Processors compute faster than they can communicate.
- Problem gets worse as number of processors increase
- Main bottleneck to parallel computing
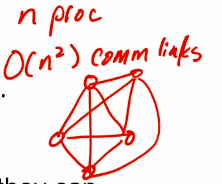
- Synchronization
- Scheduling
- Structured vs. unstructured
- Structured problems can be solved with custom hardware.
- Unstructured problems more general, but less efficient.
- Inherent linmitations
- Some problems are not( or don't seem to be ) paralleizable
- Dijkstra's shortest paths algorithm
- Other problems require clever algorithms to become parallel.
- Fibonacci series (\(a_{n}=a_{n-1}+a_{n-2}\))
- The human factor
- Hard to keep track of concurrent events and dependencies.
- Parallel algorithms are hard to design and debug.
- Some problems are not( or don't seem to be ) paralleizable
Course Outline
- Parallel architectures.
- shared memory
- distributed memory
- many more
- Parallel languages
- OpenMP
- MPI
- cuda
- MapReduce
- Algorithm design techniques
- Decomposition
- Load balancing
- schedling
## state of the art
- parellel computers today mainly based on four processor architectures.
- Multi-cores
- Many-cores
- FPGA
- ASIC
- power efficiency: goal 50GFLOPS/W
- Top-500
Shanghaitech GeekPie 2020 WarmUP CTF Game - G20G Stage 3 Doc
Stage 3
3-1 失踪的快递
湖北省武汉市某同学家。从得到一个快递号,没来的去取,上面的身份证号已经模糊,需要猜出才能取得快递。
快递编号 3102511818424 → X
百度第一次认识 Google 是什么时候 → Y
身份证号
TL;DR - 目前的选择是 42011620060523627X。
前六位
前六位为行政区域编码。
湖北武汉黄陂区
考虑到能自己少做一些就少做一些,目前看到快递单号 3102511818424 还可以:
| 3102511818424 | 湖北武汉黄陂区 | 420116 |
这个单号的优点是 直接用百度搜索 会提示“:( 抱歉,查询出错,请重试或点击快递公司官网地址进行查询。”,但实际上到韵达快递官网是能找到的。
日期部分
需要一个带有 年 月 日 的 日期。
百度第一次认识 Google 是什么时候
| 百度搜 Google | 最早结果 2001年6月30日 | 20010631 |
百度第一次删除 Google 是什么时候
可能需要一些线索提示要去“百度百科”找答案
| Google 词条编辑历史 | 最早删除 2006-05-23 | 20060523 |
其他方法
举例:
- 询问黑板报得到答案
最后四位
数字都给出来,顺序要你自己猜。选择校验码为 X,则可以使用 627X。
3-2 快递的秘密
Onion 域名
blgpxymqjoo35curmvsldxejuq5vsyf5orutrfp25bdan223t62a3vad.onion/42011620010631726X 跳转到一个教务系统的登陆界面。需要输入自己的邮箱和与之匹配的用户名登陆。之后跳转到
查看课件
ppt隐写
改ppt为zip解压出藏在最后的网址和线索
3-3 救人的药
ppt给出线索跳转到jupyter hub 的登陆界面
网址 victoryang00.xyz:5006 用户名 jupyter1-6 密码 g20
每运行一步能得到一部分分数
最后在前端输入所有可能的总共化合物的碳原子比氢原子的比值的最小值(保留13位有效数字)得到分数
此步骤有mutex 锁(显卡只有一块,而训练会allocate全部显存),即一组在运行时,另一组无法进行,也是拉大时间差距的一关
答案是 0.8235294117647
3-4 电话号码
承接上回给出的线索,以下线索按时间顺序(每10分钟)给出,要求得到电话号码
位置提示1
https://j.map.baidu.com/f3/fGw 最接近球状物体的地方

位置提示2
https://j.map.baidu.com/a2/C_w 和上一张图同时存在的地方

位置提示3
上海微小卫星工程中心
答案是 (021)50735001
[Parallel Computing] cuda 默认流&非默认流 (异步流和可视化)分析
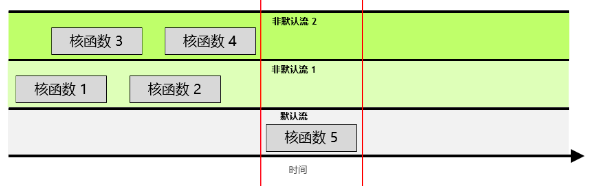
并发 cuda stream
默认流具有更高的优先级,在QuEST中默认流为Statevec_compactUnitaryKernel 函数,同时占用的gpu时间和运算重点都在此核函数上。
给定流中的操作会按序执行。
- 就不同非默认流中的操作而言,无法保证其会按彼此之间的任何特定顺序执行。
- 默认流会受到阻碍,并在其他所有流完成之后方可运行,但其亦会阻碍其他流的运行直至其自身已运行完毕。
定义非默认流,把cudaStream_t stream; 作为参数传递,让编译器自动完成默认流的创建和复制。
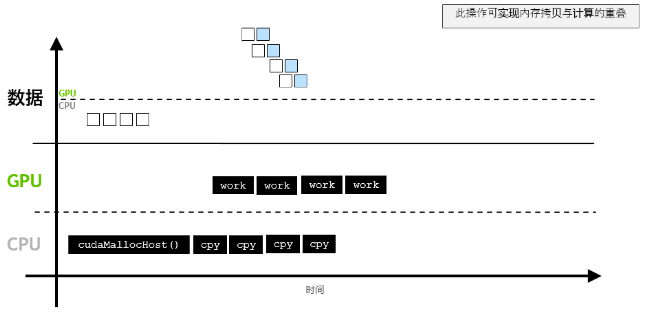
用cudaMallocManaged 和 cudaMemPrefetchAsync
更详细的内存管理:
cudaMallocGPU分配内存cudaMallocHost把内存分配在cpu上
第三个杀手锏 cudaMemcpyAsync
What does Multi-Armed Bandit means?
credit:https://iosband.github.io/2015/07/19/Efficient-experimentation-and-multi-armed-bandits.html
At first, multi-armed bandit means using
\(f^* : \mathcal{X} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}\)
- Each arm \(i\) pays out 1 dollar with probability \(p_i\) if it is played; otherwise it pays out nothing.
- While the \(p_1,…,p_k\) are fixed, we don’t know any of their values.
- Each timestep \(t\) we pick a single arm \(a_t\) to play.
- Based on our choice, we receive a return of \(r_t \sim Ber(p_{a_t})\).
- ##How should we choose arms so as to maximize total expected return?##